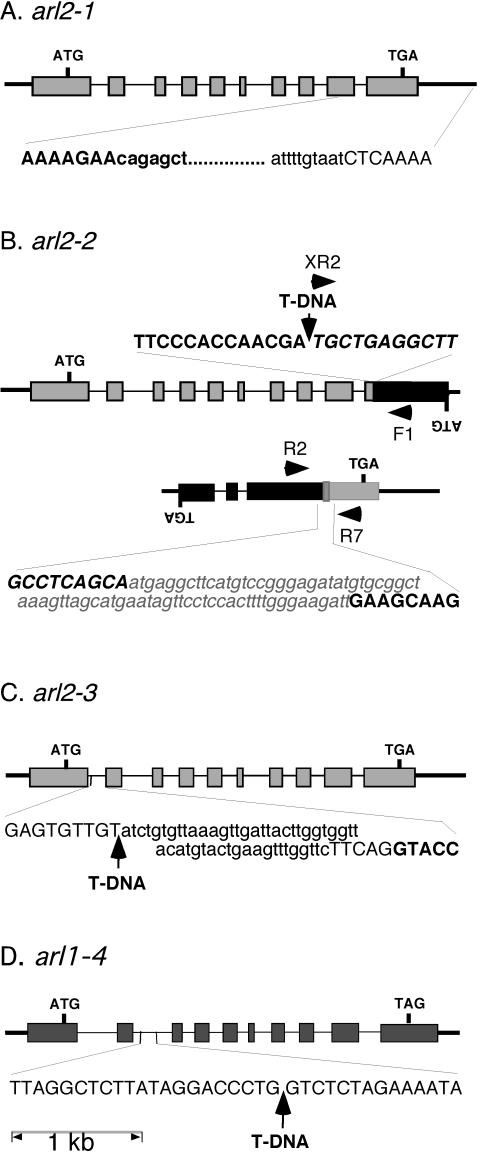
Figure 4.
Genomic structure of arl2-1 (A), arl2-2 (B), arl2-3 (C), and arl1-4 (D). Exons are represented by rectangles, introns by thin bars, and intergenic chromosomal regions by thick bars. ATG, Translation initiation codons; TGA or TAG, stop codons, ARL2 and At2g20050 or ARL1. Initiation and stop codons for lower strand open reading frames (ORFs; B) are indicated by inverted letters. The nucleotide sequence of a segment of DNA flanking the mutation site in each allele is indicated at the bottom or top of the corresponding diagram. The nucleotide sequence of an ARL2 or ARL1 exon fragment is represented in bold and uppercase characters, whereas that of an intronic or intergenic region is represented by uppercase characters. The sequence of At2g20050 exon fragments (B) is represented by italic uppercase characters. Sequences deleted within a specific allele are represented by lowercase characters, whereas new sequences added at a specific site (translocation breakpoint between the ARL2 and At2g20050 3′end fragments in arl2-2) are represented by a gray box, and written in bold, italicized, lowercase gray characters. T-DNA inserts are represented by arrows. For arl2-2 (B), the two ARL2 sequence-containing loci derived from a reciprocal translocation between chromosomes 1 and 2 are shown, along with the position of primers (black arrowheads) used in diagnostic PCR reactions (Fig. 5).