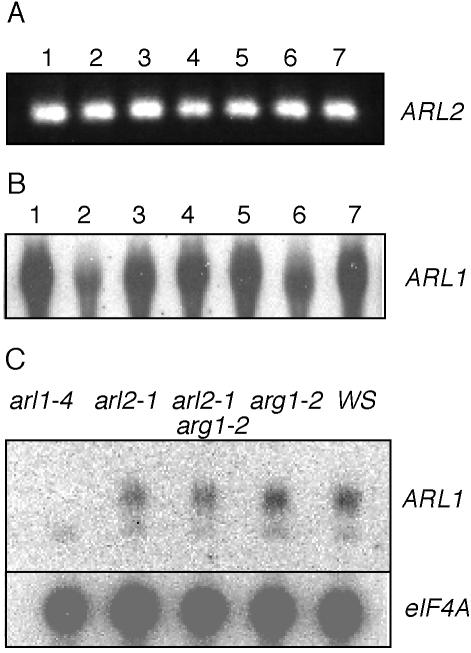
Figure 7.
The ARL2 and ARL1 genes are expressed ubiquitously in Arabidopsis seedlings and plants. A, 3′ ARL2 cDNA fragments can be reverse transcription-PCR amplified from mRNAs extracted from siliques (1), cauline leaves (3), rosette leaves (4), stems (5), and flowers (6) of mature plants, roots of 3-week-old liquid-grown plants (7), and cotyledon and leaves of 5-d-old seedlings (2). B, Northern-blot analysis of total RNAs extracted from the plant organs defined in A, using ARL1 cDNA as a probe. Twenty micrograms of total RNA was loaded in each lane. C, Northern-blot analysis of total RNAs extracted from arl1-4, arl2-1, arg1-2 arl2-1, arg1-2, and wild-type Ws seedlings, using ARL1 (upper) or eIF4A (lower; loading control) cDNA sequences as probes. In this experiment, the ARL1 probe detected a low-intensity, nonspecific signal in all RNAs tested (including arl1-4). However, the specific ARL1 signal was not detectable in RNAs extracted from arl1-4 seedlings. In each panel, the source of mRNA is indicated above each lane, whereas the probe is identified at the right of the panel.