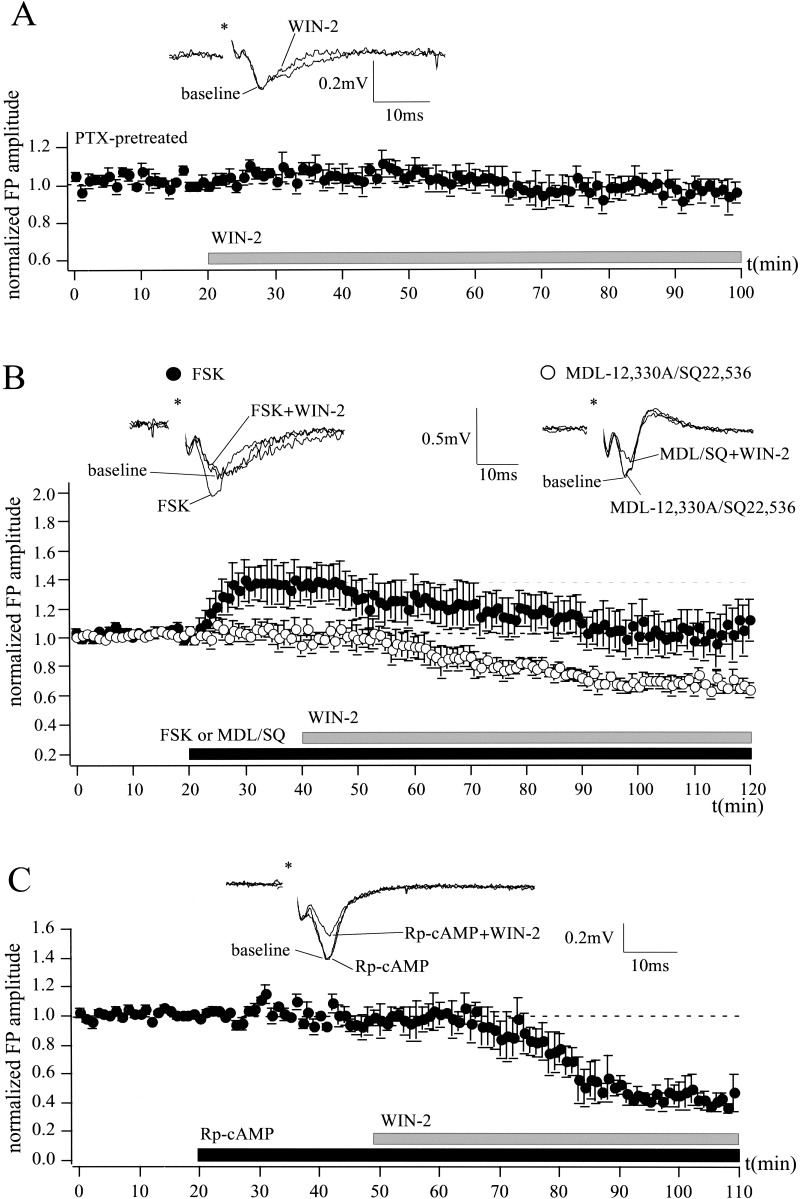
Figure 6.
Cannabinoid action in the LA involves the activation of Gi/o proteins, but not the inhibition of the AC-PKA pathway. (A) Preincubation of slices with the Gi/o protein inhibitor PTX (5 μg/mL) for 5–7 h abolishes the effects of WIN-2 (5 μM) on extracellularly recorded FP amplitudes (WIN-2, 95 ± 6% of baseline; n = 6; P > 0.05). (B) Application of the AC activator FSK (10 μM), but not of the AC inhibitors MDL-12,330A (10 μM) and SQ 22,536 (50 μM), rapidly increases FP amplitude to 139 ± 12% of baseline (n = 7; P > 0.05). Neither the AC activator (FSK, 100%; FSK + WIN-2, 66 ± 9%; n = 7; P < 0.05), nor the AC inhibitors (MDL/SQ, 100%; MDL/SQ + WIN-2, 63 ± 6%; n = 7; P < 0.05) alter WIN-2-induced reduction of FP amplitude. (C) Inhibition of the PKA by Rp-cAMP (25 μM) does not prevent WIN-2 action on synaptic transmission (Rp-cAMP, 100%; Rp-cAMP + WIN-2, 49 ± 10%; n = 4; P < 0.05). Representative traces are shown. All data are normalized to the respective baseline values (last 10 min of baseline). Asterisks mark stimulation artifacts.