Abstract
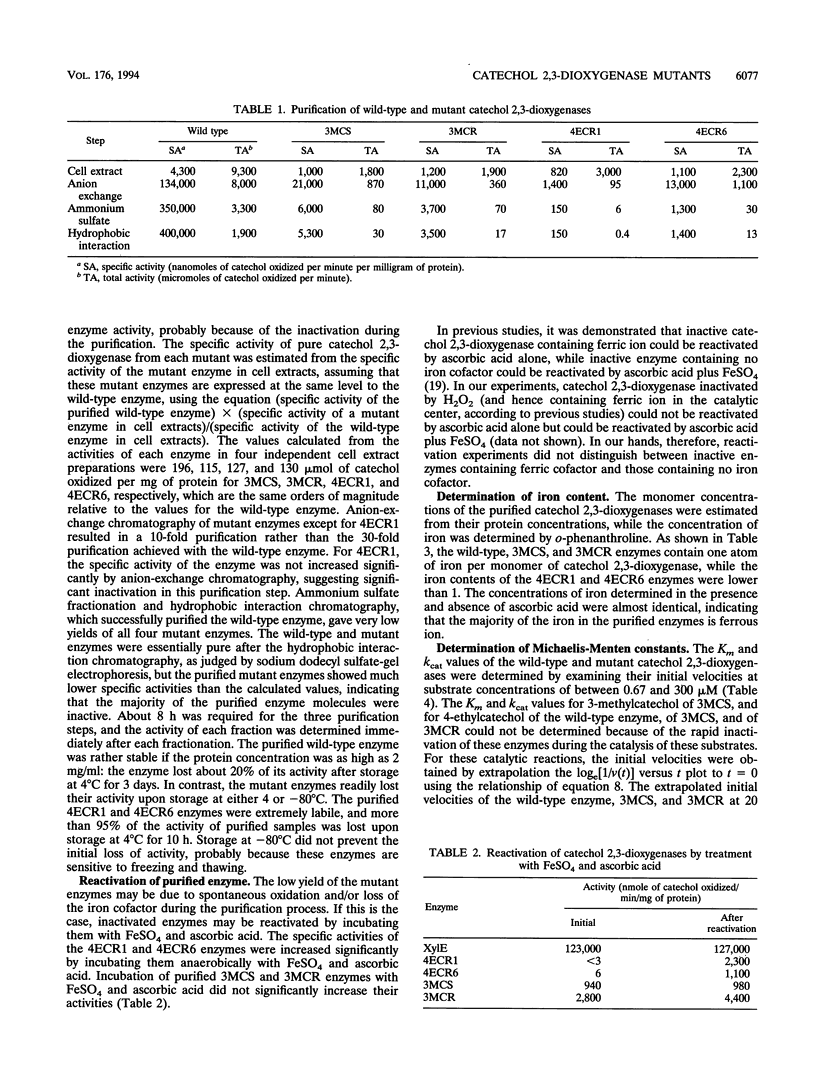
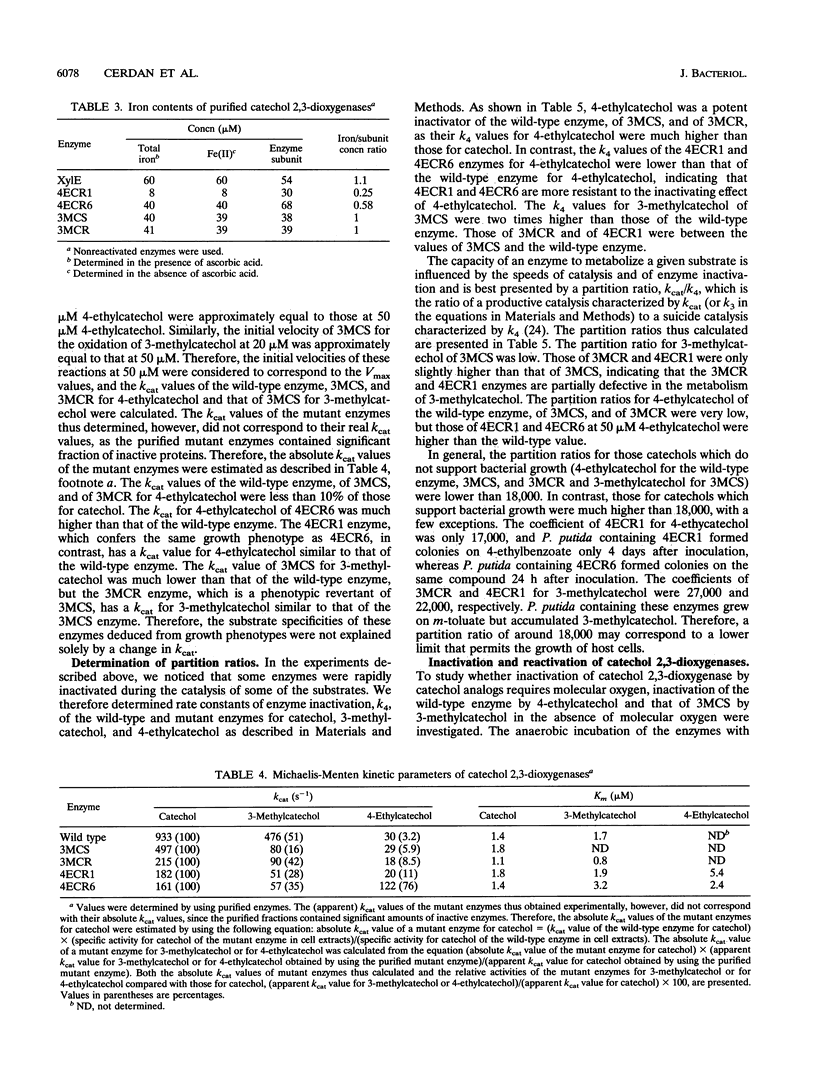
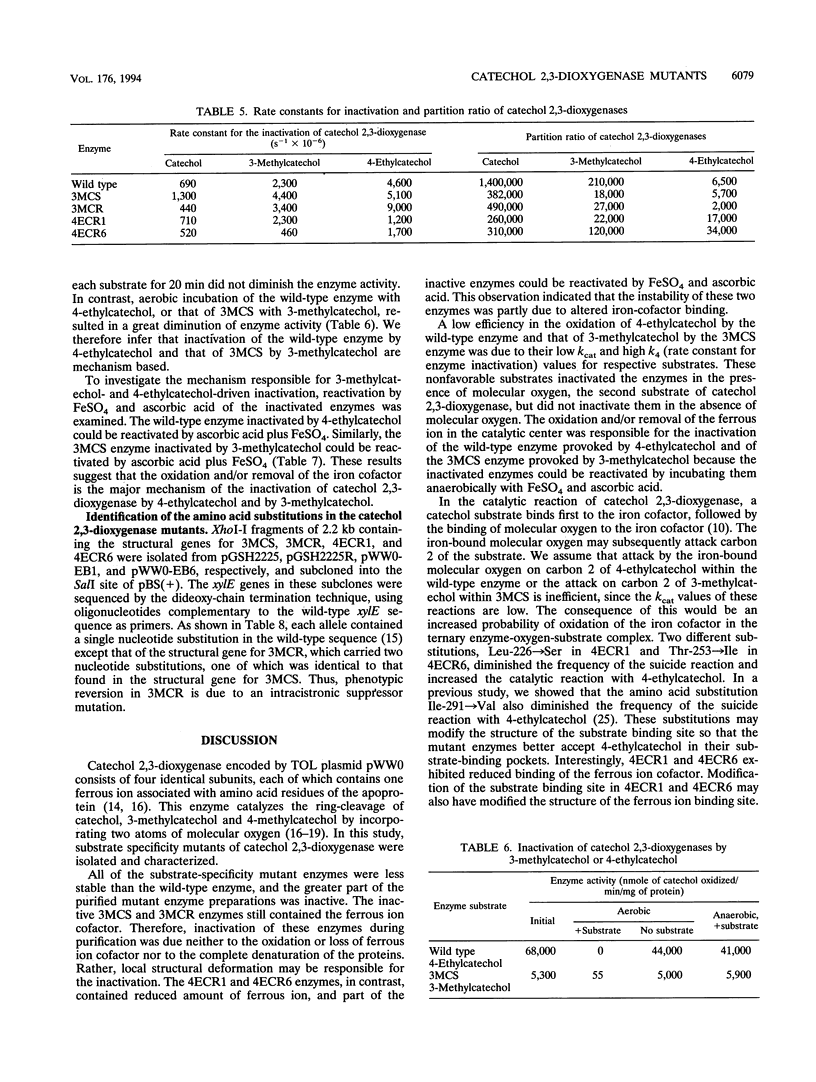
Catechol 2,3-dioxygenase encoded by TOL plasmid pWW0 of Pseudomonas putida consists of four identical subunits, each containing one ferrous ion. The enzyme catalyzes ring cleavage of catechol, 3-methylcatechol, and 4-methylcatechol but shows only weak activity toward 4-ethylcatechol. Two mutants of catechol 2,3-dioxygenases (4ECR1 and 4ECR6) able to oxidize 4-ethylcatechol, one mutant (3MCS) which exhibits only weak activity toward 3-methylcatechol but retained the ability to cleave catechol and 4-methylcatechol, and one phenotypic revertant of 3MCS (3MCR) which had regained the ability to oxidize 3-methylcatechol were characterized by determining their Km and partition ratio (the ratio of productive catalysis to suicide catalysis). The amino acid substitutions in the four mutant enzymes were also identified by sequencing their structural genes. Wild-type catechol 2,3-dioxygenase was inactivated during the catalysis of 4-ethylcatechol and thus had a low partition ratio for this substrate, whereas the two mutant enzymes, 4ECR1 and 4ECR6, had higher partition ratios for it. Similarly, mutant enzyme 3MCS had a lower partition ratio for 3-methylcatechol than that of 3MCR. Molecular oxygen was required for the inactivation of the wild-type enzyme by 4-ethylcatechol and of 3MCS by 3-methylcatechol, and the inactivated enzymes could be reactivated by incubation with FeSO4 plus ascorbic acid. The enzyme inactivation is thus most likely mechanism based and occurred principally by oxidation and/or removal of the ferrous ion in the catalytic center. In general, partition ratios for catechols lower than 18,000 did not support bacterial growth. A possible meaning of the critical value of the partition ratio is discussed.
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abril M. A., Michan C., Timmis K. N., Ramos J. L. Regulator and enzyme specificities of the TOL plasmid-encoded upper pathway for degradation of aromatic hydrocarbons and expansion of the substrate range of the pathway. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6782–6790. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6782-6790.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall B. G. Directed evolution of a bacterial operon. Bioessays. 1990 Nov;12(11):551–558. doi: 10.1002/bies.950121109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. B., Olsen R. H. Isolation of large bacterial plasmids and characterization of the P2 incompatibility group plasmids pMG1 and pMG5. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):227–238. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.227-238.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harayama S., Kok M., Neidle E. L. Functional and evolutionary relationships among diverse oxygenases. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1992;46:565–601. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.46.100192.003025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harayama S., Leppik R. A., Rekik M., Mermod N., Lehrbach P. R., Reineke W., Timmis K. N. Gene order of the TOL catabolic plasmid upper pathway operon and oxidation of both toluene and benzyl alcohol by the xylA product. J Bacteriol. 1986 Aug;167(2):455–461. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.2.455-461.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MASSEY V. Studies on succinic dehydrogenase. VII. Valency state of the iron in beef heart succinic dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1957 Dec;229(2):763–770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mermod N., Lehrbach P. R., Reineke W., Timmis K. N. Transcription of the TOL plasmid toluate catabolic pathway operon of Pseudomonas putida is determined by a pair of co-ordinately and positively regulated overlapping promoters. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2461–2466. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02156.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai C., Hori K., Kagamiyama H., Nakazawa T., Nozaki M. Purification, subunit structure, and partial amino acid sequence of metapyrocatechase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):2916–2922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakai C., Kagamiyama H., Nozaki M., Nakazawa T., Inouye S., Ebina Y., Nakazawa A. Complete nucleotide sequence of the metapyrocatechase gene on the TOI plasmid of Pseudomonas putida mt-2. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):2923–2928. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nozaki M., Kotani S., Ono K., Seno S. Metapyrocatechase. 3. Substrate specificity and mode of ring fission. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Nov 11;220(2):213–223. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(70)90007-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nozaki M., Ono K., Nakazawa T., Kotani S., Hayaishi O. Metapyrocatechase. II. The role of iron and sulfhydryl groups. J Biol Chem. 1968 May 25;243(10):2682–2690. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nozaki M. Oxygenases and dioxygenases. Top Curr Chem. 1979;78:145–186. doi: 10.1007/BFb0048193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Polissi A., Harayama S. In vivo reactivation of catechol 2,3-dioxygenase mediated by a chloroplast-type ferredoxin: a bacterial strategy to expand the substrate specificity of aromatic degradative pathways. EMBO J. 1993 Aug;12(8):3339–3347. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06004.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos J. L., Stolz A., Reineke W., Timmis K. N. Altered effector specificities in regulators of gene expression: TOL plasmid xylS mutants and their use to engineer expansion of the range of aromatics degraded by bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8467–8471. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos J. L., Wasserfallen A., Rose K., Timmis K. N. Redesigning metabolic routes: manipulation of TOL plasmid pathway for catabolism of alkylbenzoates. Science. 1987 Jan 30;235(4788):593–596. doi: 10.1126/science.3468623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams P. A., Assinder S. J., Shaw L. E. Construction of hybrid xylE genes between the two duplicate homologous genes from TOL plasmid pWW53: comparison of the kinetic properties of the gene products. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Aug;136(8):1583–1589. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-8-1583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worsey M. J., Franklin F. C., Williams P. A. Regulation of the degradative pathway enzymes coded for by the TOL plasmid (pWWO) from Pseudomonas putida mt-2. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):757–764. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.757-764.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


