Abstract
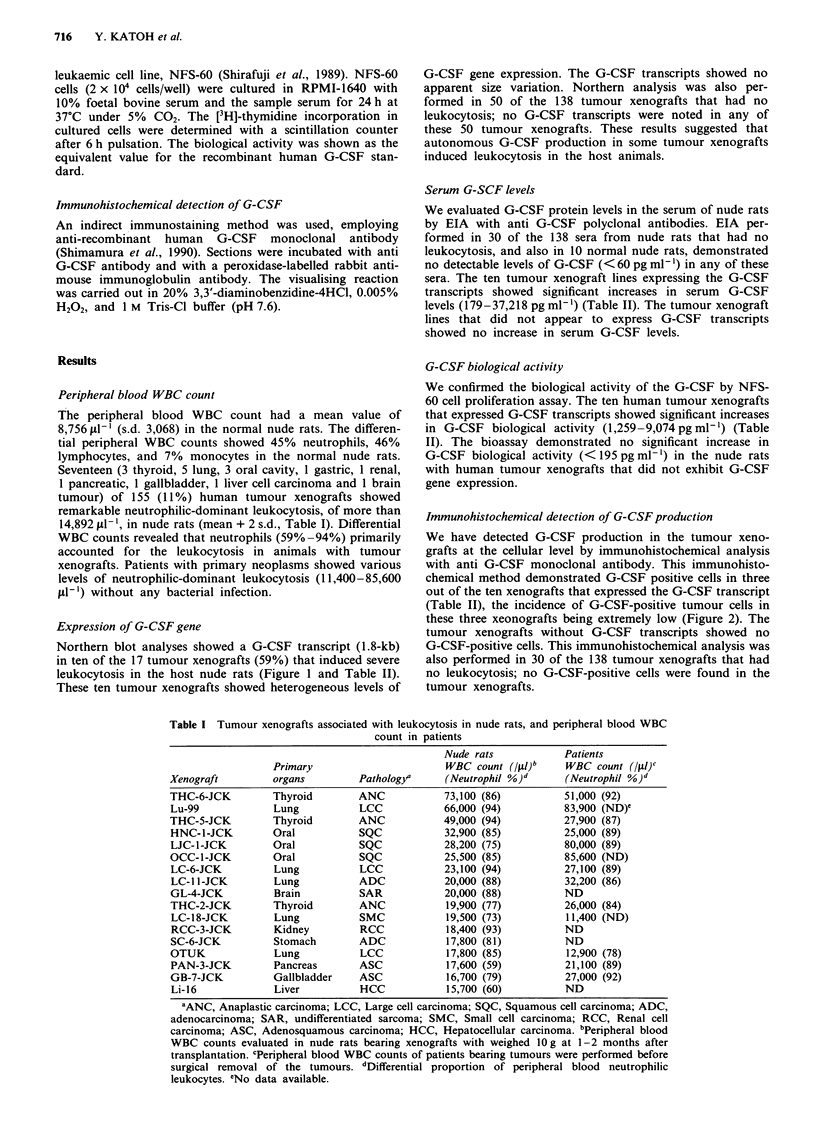
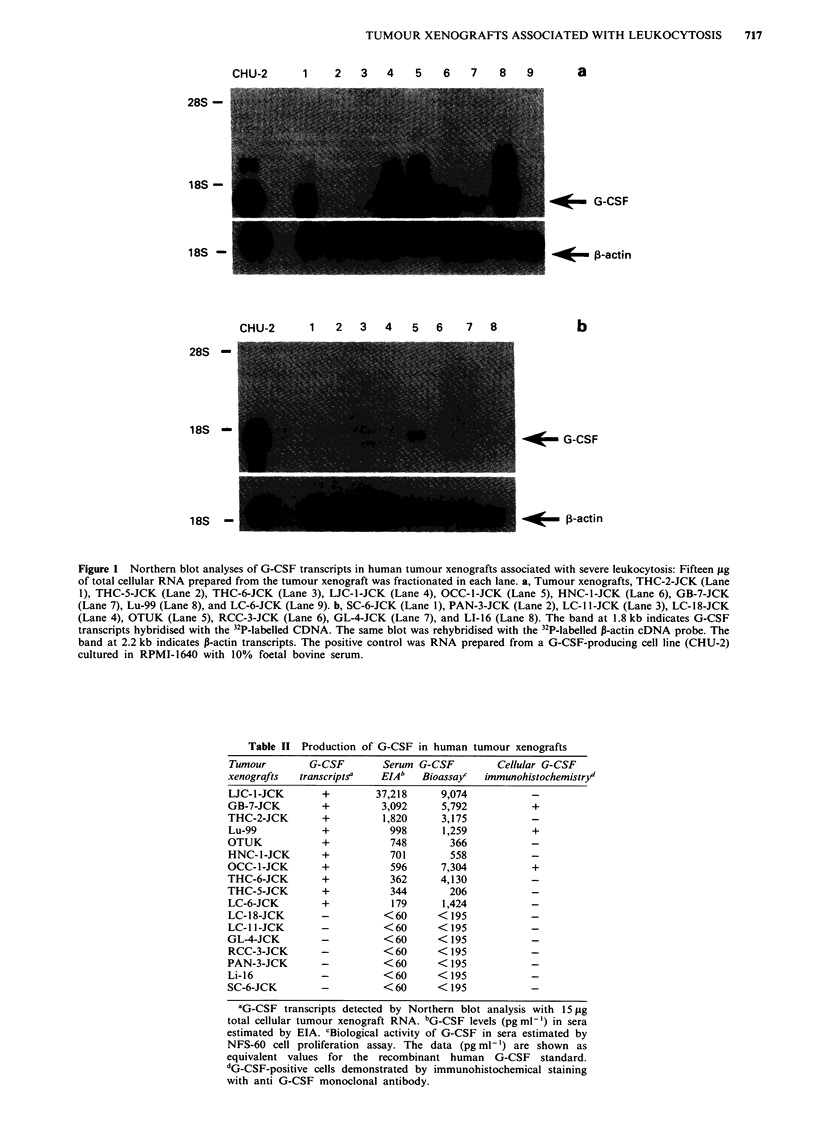
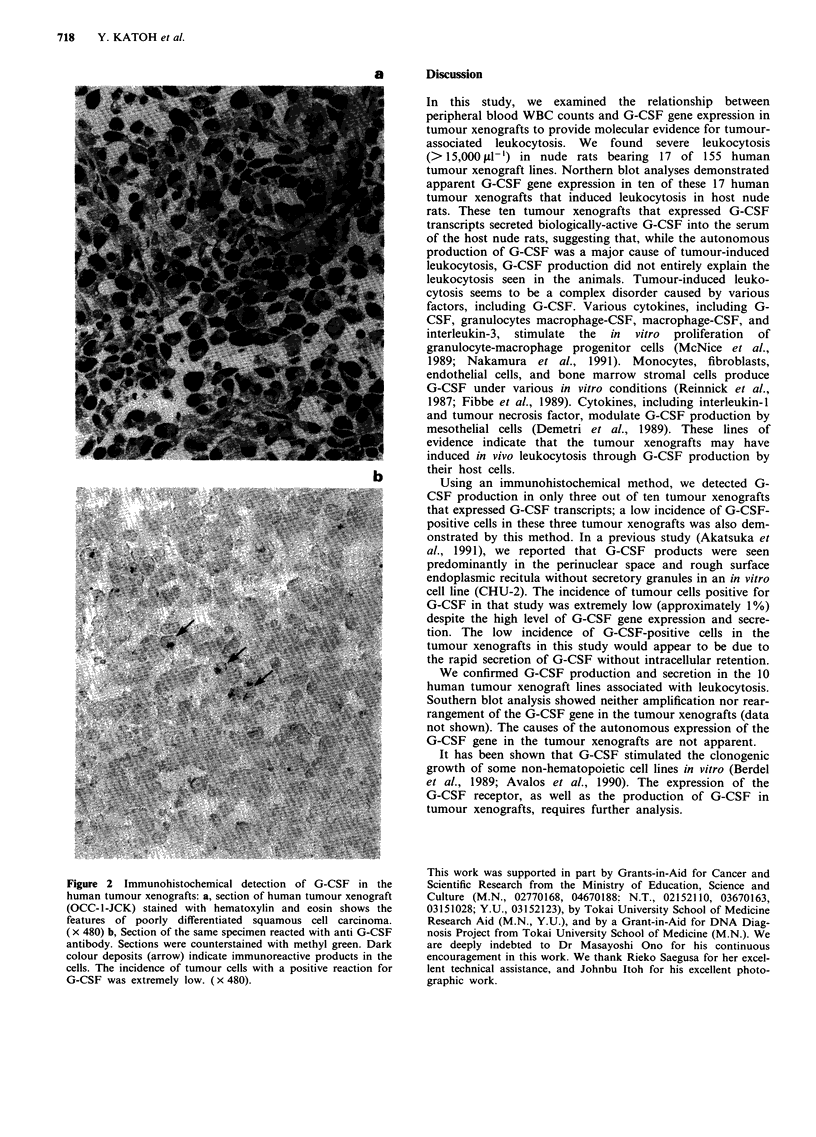
Leukocytosis sometimes accompanies malignant neoplasms in the absence of infection. It is thought that the production of colony-stimulating factor by neoplasms is the most potent cause of tumour-induced leukocytosis; several mechanisms have been suggested to explain this. We examined 155 human tumour xenografts established in nude mice, and found that 17 of the xenografts induced remarkable leukocytosis (> 15,000 microliters-1) in nude rats. We examined granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) production by the xenografts to study the mechanisms underlying this tumour-induced leukocytosis. Ten of the 17 xenografted human tumours appeared to express the G-CSF gene. Serum G-CSF increased, to concentrations of 179-37,218 pg ml-1, in host animals transplanted with the ten xenografts expressing the G-CSF gene transcripts. The biological activity of serum G-CSF also increased, to concentrations of 206-9,074 pg ml-1, in the host animals transplanted with the ten xenografts. Immunohistochemical analysis demonstrated G-CSF production at the cellular level in three of the ten xenografts. These results suggested that the production of G-CSF is a common event in human tumour xenografts associated with leukocytosis, but that factors other than G-CSF are also likely to be involved. Leukocytosis induced by neoplasms seems to be a heterogeneous and complex disorder.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akatsuka A., Shimamura K., Katoh Y., Takekoshi S., Nakamura M., Nomura H., Hasegawa M., Ueyama Y., Tamaoki N. Electron microscopic identification of the intracellular secretion pathway of human G-CSF in a human tumor cell line: a comparative study with a Chinese hamster ovary cell line (IA1-7) transfected with human G-CSF cDNA. Exp Hematol. 1991 Sep;19(8):768–772. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asano S., Urabe A., Okabe T., Sato N., Kondo Y. Demonstration of granulopoietic factor(s) in the plasma of nude mice transplanted with a human lung cancer and in the tumor tissue. Blood. 1977 May;49(5):845–852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avalos B. R., Gasson J. C., Hedvat C., Quan S. G., Baldwin G. C., Weisbart R. H., Williams R. E., Golde D. W., DiPersio J. F. Human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor: biologic activities and receptor characterization on hematopoietic cells and small cell lung cancer cell lines. Blood. 1990 Feb 15;75(4):851–857. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berdel W. E., Danhauser-Riedl S., Steinhauser G., Winton E. F. Various human hematopoietic growth factors (interleukin-3, GM-CSF, G-CSF) stimulate clonal growth of nonhematopoietic tumor cells. Blood. 1989 Jan;73(1):80–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Demetri G. D., Zenzie B. W., Rheinwald J. G., Griffin J. D. Expression of colony-stimulating factor genes by normal human mesothelial cells and human malignant mesothelioma cells lines in vitro. Blood. 1989 Aug 15;74(3):940–946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fibbe W. E., Daha M. R., Hiemstra P. S., Duinkerken N., Lurvink E., Ralph P., Altrock B. W., Kaushansky K., Willemze R., Falkenburg J. H. Interleukin 1 and poly(rI).poly(rC) induce production of granulocyte CSF, macrophage CSF, and granulocyte-macrophage CSF by human endothelial cells. Exp Hematol. 1989 Mar;17(3):229–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee M. Y., Kaushansky K., Judkins S. A., Lottsfeldt J. L., Waheed A., Shadduck R. K. Mechanisms of tumor-induced neutrophilia: constitutive production of colony-stimulating factors and their synergistic actions. Blood. 1989 Jul;74(1):115–122. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNiece I., Andrews R., Stewart M., Clark S., Boone T., Quesenberry P. Action of interleukin-3, G-CSF, and GM-CSF on highly enriched human hematopoietic progenitor cells: synergistic interaction of GM-CSF plus G-CSF. Blood. 1989 Jul;74(1):110–114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motojima H., Kobayashi T., Shimane M., Kamachi S., Fukushima M. Quantitative enzyme immunoassay for human granulocyte colony stimulating factor (G-CSF). J Immunol Methods. 1989 Mar 31;118(2):187–192. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(89)90005-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagata S., Tsuchiya M., Asano S., Kaziro Y., Yamazaki T., Yamamoto O., Hirata Y., Kubota N., Oheda M., Nomura H. Molecular cloning and expression of cDNA for human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. 1986 Jan 30-Feb 5Nature. 319(6052):415–418. doi: 10.1038/319415a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura K., Takahashi T., Tsuyuoka R., Ueda Y., Suzuki A., Okuno Y., Ihara Y., Seko S., Okada T., Kumagai N. Identification of colony-stimulating factor activity in patients with malignant tumors associated with excessive leukocytosis. Jpn J Clin Oncol. 1991 Dec;21(6):395–399. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura H., Imazeki I., Oheda M., Kubota N., Tamura M., Ono M., Ueyama Y., Asano S. Purification and characterization of human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF). EMBO J. 1986 May;5(5):871–876. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1986.tb04297.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rennick D., Yang G., Gemmell L., Lee F. Control of hemopoiesis by a bone marrow stromal cell clone: lipopolysaccharide- and interleukin-1-inducible production of colony-stimulating factors. Blood. 1987 Feb;69(2):682–691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato N., Asano S., Ueyama Y., Mori M., Okabe T., Kondo Y., Ohsawa N., Kosaka K. Granulocytosis and colony-stimulating activity (CSA) produced by a human squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer. 1979 Feb;43(2):605–610. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(197902)43:2<605::aid-cncr2820430230>3.0.co;2-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimamura K., Fujimoto J., Hata J., Akatsuka A., Ueyama Y., Watanabe T., Tamaoki N. Establishment of specific monoclonal antibodies against recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (hG-CSF) and their application for immunoperoxidase staining of paraffin-embedded sections. J Histochem Cytochem. 1990 Feb;38(2):283–286. doi: 10.1177/38.2.1688901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirafuji N., Asano S., Matsuda S., Watari K., Takaku F., Nagata S. A new bioassay for human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (hG-CSF) using murine myeloblastic NFS-60 cells as targets and estimation of its levels in sera from normal healthy persons and patients with infectious and hematological disorders. Exp Hematol. 1989 Feb;17(2):116–119. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





