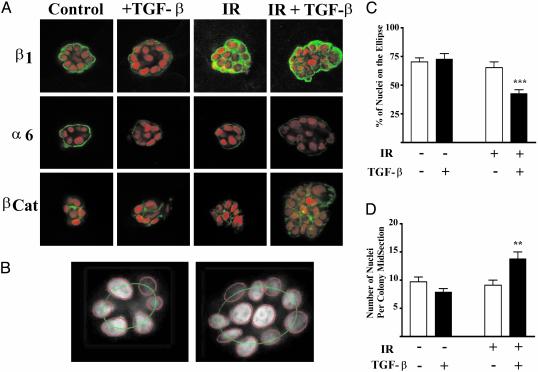
Fig. 1.
Perturbed protein localization and acinar organization as a function of TGF-β, IR, and dual treatment. Colonies develop and organize in 3D rBM culture over the course of 10 days, during which time the cells are fed every other day. EGF, to stimulate proliferation, is removed at day 6, and the cells are harvested at day 10. (A) Representative images of colonies from control, TGF-β-, IR-, or dual-treated cultures. The image is representative of the mean intensity for each marker based on image analysis of 20 randomly chosen colonies. Immunostaining of β1 integrin, α6 integrin, and β-catenin was detected by using secondary antibodies labeled with Alexa Fluor 488 (green). Nuclei are counterstained with TO-PROR-3 iodide, shown in red. Note the loss of acinar organization in the irradiated colonies. (B) Acinar organization was measured by nuclear segmentation of the colony confocal midsection fit to an ellipse as shown for a control (Left) and dual-treated (Right) colony. (C) Acinar organization as a function of treatment group (n > 100 colonies per treatment). Acinar organization was significantly (P < 0.0001) decreased in colonies that arose from irradiated cells that were cultured in the presence of TGF-β.(D) The number of nuclei per colony midsection as a function of treatment group. The number of nuclei was significantly (P < 0.001) increased in colonies arising from irradiated cells treated with TGF-β.