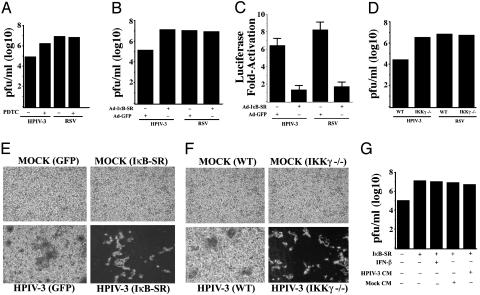
Fig. 2.
Inhibition of NF-κB activation increases HPIV-3, but not RSV, replication and cytopathogenicity in an IFN- and/or soluble factor(s)-independent manner. Plaque assay analysis using medium supernatants from A549 cells mock infected or infected with either HPIV-3 or RSV in the absence or presence of PDTC (50 μM) (A), or A549 cells infected with HPIV-3 or RSV in the absence or presence of prior infection with Ads encoding the IκB-SR or GFP(B). (C) Expression of transfected NF-κB-Luc in A549 cells infected with HPIV-3 or RSV in the presence of IκB-SR or control GFP. (D) Plaque assay analysis using medium supernatants from IKKγ–/– or WT MEFs infected with either HPIV-3 or RSV. Phase contrast microscopic picture of CV-1 cells incubated with same dilutions of medium supernatants obtained from A549 cells infected with HPIV-3 and Ad-GFP or Ad-IκB-SR (E) and HPIV-3-infected WT or IKKγ–/– MEFs (F). (G) Plaque assay analysis using medium supernatants from A549 cells infected with HPIV-3 and Ad-GFP or Ad-IκB-SR and treated with IFN-β (2,000 units/ml). Similar analysis was performed with medium supernatants from A549 cells infected with HPIV-3 and Ad-GFP or Ad-IκB-SR in the presence or absence of either mock CM or HPIV-3 CM (cleared free of virus).