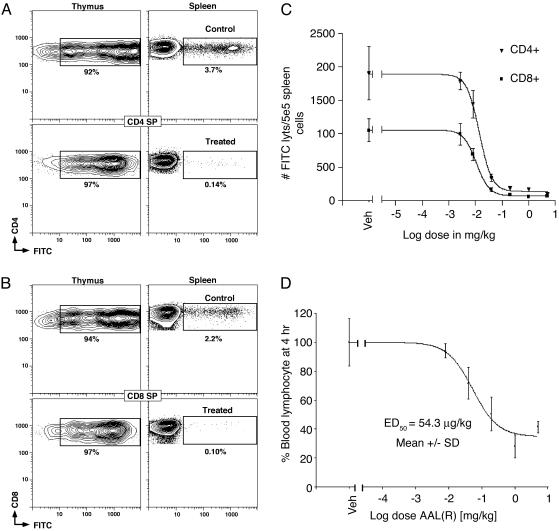
Fig. 4.
Inhibition of thymic egress by S1P receptor agonist. AAL-(R) or vehicle was administered 1 h after IT injection of FITC. The migration of recent thymic CD4 SP (A) and CD8 SP (B) emigrants to spleen was measured by flow cytometry 24 h after IT labeling (n = 5, mean ± SD). FITC was used to monitor thymic emigrants, and APC-αCD62L (MEL14) replaced APC-αCD44. AAL-(S) at 5 mg/kg was not statistically different to vehicle control. The dose–responses for inhibition of thymic egress of both CD4 and CD8 SP T cells by AAL-(R) (R2 = 0.996) (C) were similar in potency and steepness to the loss of CD69 (Fig. 3B). Mice had similar numbers of total T cells. (D) Dose–response for peripheral blood lymphopenia induced by AAL-(R).