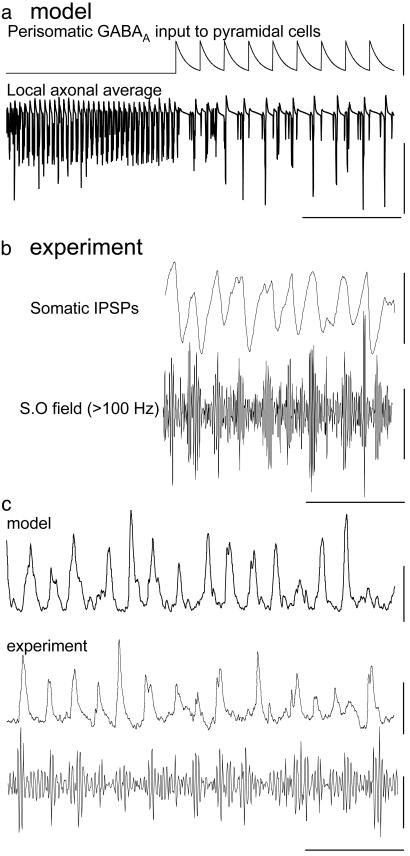
Fig. 4.
Pattern of collective axonal behavior induced by kainate during gamma field oscillations is GABAA receptor-dependent: reciprocal interaction with interneurons. (a) Model data (intact network with recurrent synapses blocked) showing local axonal average in response to an ectopic rate of 1 per axon per s (compare with Fig. 2aii). During the initial part of the trace no perisomatic inhibition is present, and then a 40-Hz train of perisomatic inhibitory synaptic events was fed into the system. It should be noted that these events were generated exogenously, not as part of the collective behavior of the entire network. Perisomatic synaptic inhibition at 40 Hz modulated the collective axonal behavior in a manner closely resembling that seen in the intact model (Fig. 2ai). (Scale bars: Upper,40nS; Lower, 40 mV and 100 ms.) (b) Concurrent experimental recordings of somatic IPSP (from a membrane potential of –30 mV; Upper) and high-pass-filtered stratum oriens field (Lower). Note the occurrence of activity on the decay phase of IPSPs, terminated by the onset of the subsequent IPSP. S.O field, stratum oriens field. (Scale bars: Upper, 6 mV; Lower, 10 μV and 100 ms.) (c) Collective axonal behavior generates compound EPSPs in fast-spiking interneurons in CA1 stratum pyramidale during field gamma oscillations in the intact CA1 sections (cell impaled with electrodes containing 50 mM QX314 to block action potentials and hyperpolarized to –70 mV). Superimposed below is the concurrent stratum oriens field recording high-pass-filtered at 100 Hz. This pattern of behavior is identical to that seen in the intact model for total α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid receptor-mediated input to an interneuron. Model ectopic rate, 1 per s per pyramidal cell axon. (Scale bars: Top, 4 nS; Middle, 5 mV; Bottom, 10 μV and 100 ms.)