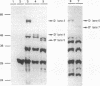
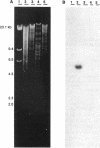
Abstract
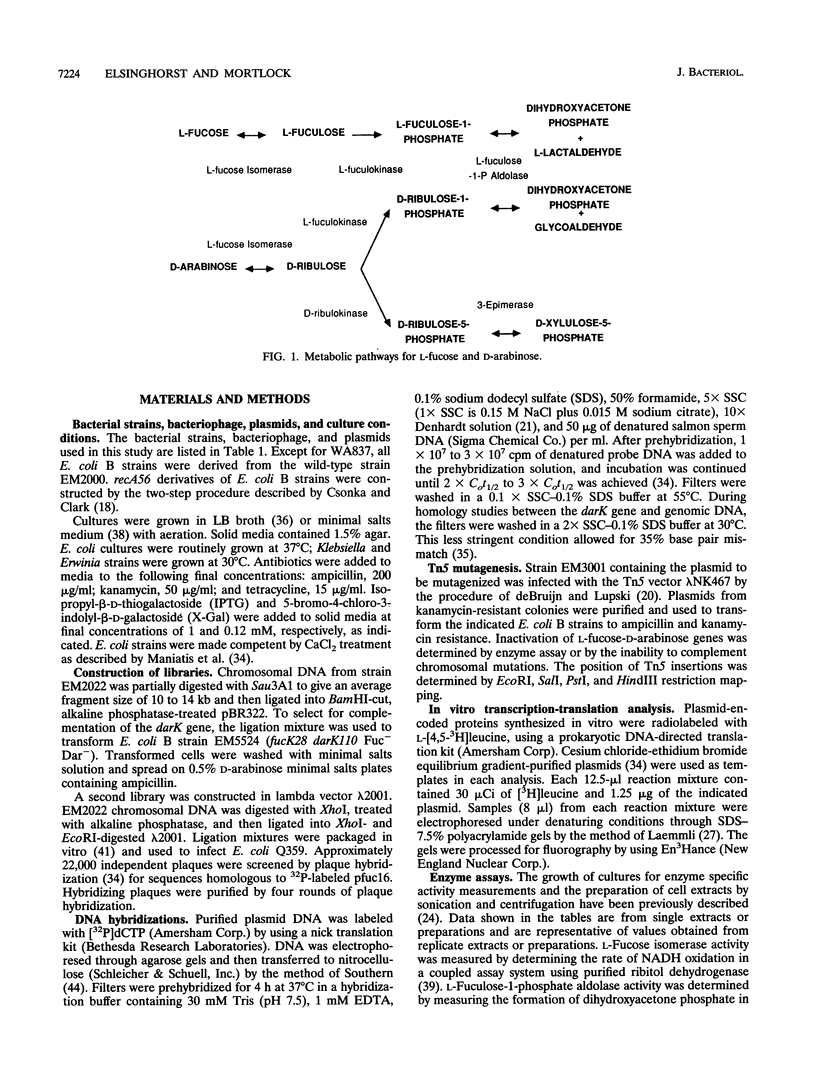
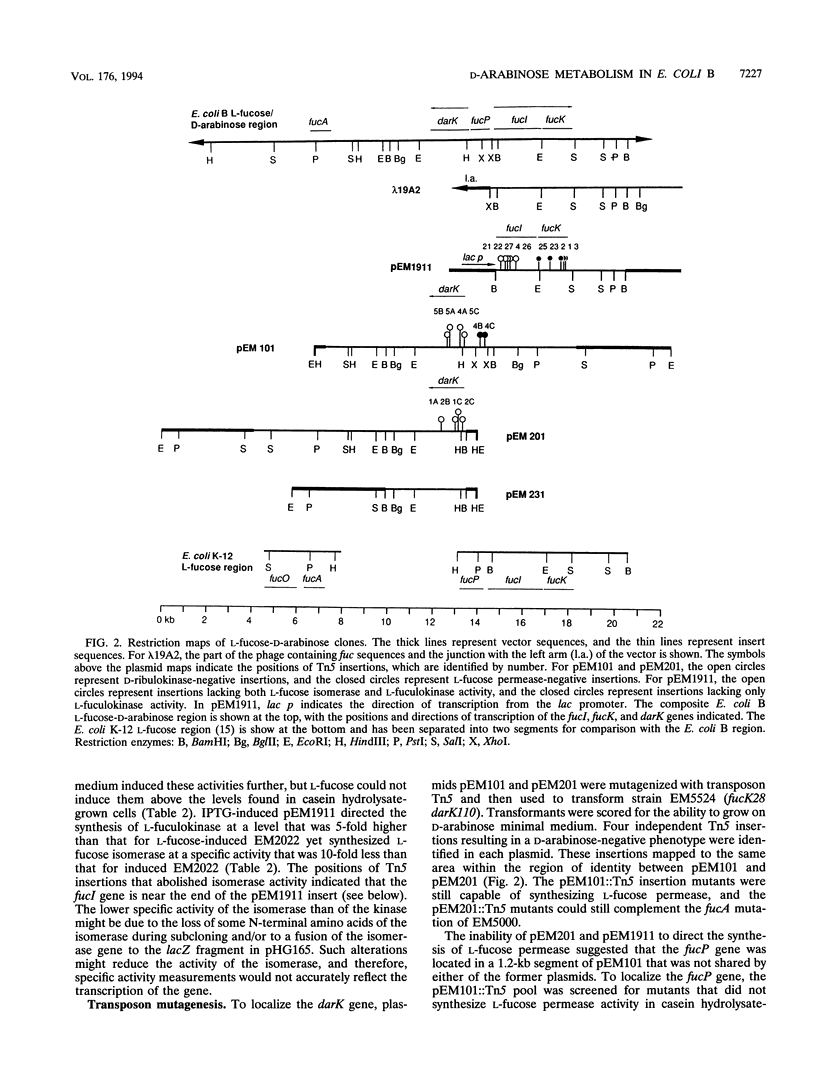
To metabolize the uncommon pentose D-arabinose, enteric bacteria often recruit the enzymes of the L-fucose pathway by a regulatory mutation. However, Escherichia coli B can grow on D-arabinose without the requirement of a mutation, using some of the L-fucose enzymes and a D-ribulokinase that is distinct from the L-fuculokinase of the L-fucose pathway. To study this naturally occurring D-arabinose pathway, we cloned and partially characterized the E. coli B L-fucose-D-arabinose gene cluster and compared it with the L-fucose gene cluster of E. coli K-12. The order of the fucA, -P, -I, and -K genes was the same in the two E. coli strains. However, the E. coli B gene cluster contained a 5.2-kb segment located between the fucA and fucP genes that was not present in E. coli K-12. This segment carried the darK gene, which encodes the D-ribulokinase needed for growth on D-arabinose by E. coli B. The darK gene was not homologous with any of the L-fucose genes or with chromosomal DNA from other D-arabinose-utilizing bacteria. D-Ribulokinase and L-fuculokinase were purified to apparent homogeneity and partially characterized. The molecular weights, substrate specificities, and kinetic parameters of these two enzymes were very dissimilar, which together with DNA hybridization analysis, suggested that these enzymes are not related. D-Arabinose metabolism by E. coli B appears to be the result of acquisitive evolution, but the source of the darK gene has not been determined.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ANDERSON R. L., WOOD W. A. Purification and properties of L-xylulokinase. J Biol Chem. 1962 Apr;237:1029–1033. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Appleyard R K. Segregation of New Lysogenic Types during Growth of a Doubly Lysogenic Strain Derived from Escherichia Coli K12. Genetics. 1954 Jul;39(4):440–452. doi: 10.1093/genetics/39.4.440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartkus J. M., Mortlock R. P. Construction of an improved D-arabinose pathway in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):704–709. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.704-709.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartkus J. M., Mortlock R. P. Isolation of a mutation resulting in constitutive synthesis of L-fucose catabolic enzymes. J Bacteriol. 1986 Mar;165(3):710–714. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.3.710-714.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bisson T. M., Oliver E. J., Mortlock R. P. Regulation of pentitol metabolism by aerobacter aerogenes. II. Induction of the ribitol pathway. J Bacteriol. 1968 Mar;95(3):932–936. doi: 10.1128/jb.95.3.932-936.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulter J. R., Gielow W. O. Properties of D-arabinose isomerase purified from two strains of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):687–696. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.687-696.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boulter J., Gielow B., McFarland M., Lee N. Metabolism of D-arabinose by Escherichia coli B-r. J Bacteriol. 1974 Feb;117(2):920–923. doi: 10.1128/jb.117.2.920-923.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1006/abio.1976.9999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bryan J. K. Molecular weights of protein multimers from polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Anal Biochem. 1977 Apr;78(2):513–519. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90111-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakrabarti T., Chen Y. M., Lin E. C. Clustering of genes for L-fucose dissimilation by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Mar;157(3):984–986. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.3.984-986.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. M., Lu Z., Lin E. C. Constitutive activation of the fucAO operon and silencing of the divergently transcribed fucPIK operon by an IS5 element in Escherichia coli mutants selected for growth on L-1,2-propanediol. J Bacteriol. 1989 Nov;171(11):6097–6105. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.11.6097-6105.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. M., Tobin J. F., Zhu Y., Schleif R. F., Lin E. C. Cross-induction of the L-fucose system by L-rhamnose in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3712–3719. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3712-3719.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. M., Zhu Y., Lin E. C. The organization of the fuc regulon specifying L-fucose dissimilation in Escherichia coli K12 as determined by gene cloning. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Dec;210(2):331–337. doi: 10.1007/BF00325702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cocks G. T., Aguilar T., Lin E. C. Evolution of L-1, 2-propanediol catabolism in Escherichia coli by recruitment of enzymes for L-fucose and L-lactate metabolism. J Bacteriol. 1974 Apr;118(1):83–88. doi: 10.1128/jb.118.1.83-88.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornish-Bowden A., Eisenthal R. Statistical considerations in the estimation of enzyme kinetic parameters by the direct linear plot andother methods. Biochem J. 1974 Jun;139(3):721–730. doi: 10.1042/bj1390721. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csonka L. N., Clark A. J. Construction of an Hfr strain useful for transferring recA mutations between Escherichia coli strains. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):529–530. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.529-530.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DAVIS B. J. DISC ELECTROPHORESIS. II. METHOD AND APPLICATION TO HUMAN SERUM PROTEINS. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1964 Dec 28;121:404–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1964.tb14213.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denhardt D. T. A membrane-filter technique for the detection of complementary DNA. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Jun 13;23(5):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90447-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doten R. C., Mortlock R. P. Directed evolution of a second xylitol catabolic pathway in Klebsiella pneumoniae. J Bacteriol. 1984 Aug;159(2):730–735. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.2.730-735.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doten R. C., Mortlock R. P. Production of D- and L-xylulose by mutants of Klebsiella pneumoniae and Erwinia uredovora. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jan;49(1):158–162. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.1.158-162.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsinghorst E. A., Mortlock R. P. D-arabinose metabolism in Escherichia coli B: induction and cotransductional mapping of the L-fucose-D-arabinose pathway enzymes. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5423–5432. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5423-5432.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karn J., Brenner S., Barnett L., Cesareni G. Novel bacteriophage lambda cloning vector. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5172–5176. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karn J., Matthes H. W., Gait M. J., Brenner S. A new selective phage cloning vector, lambda 2001, with sites for XbaI, BamHI, HindIII, EcoRI, SstI and XhoI. Gene. 1984 Dec;32(1-2):217–224. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90049-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBlanc D. J., Mortlock R. P. Metabolism of D-arabinose: a new pathway in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1971 Apr;106(1):90–96. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.1.90-96.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LeBlanc D. J., Mortlock R. P. Metabolism of D-arabinose: origin of a D-ribulokinase activity in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1971 Apr;106(1):82–89. doi: 10.1128/jb.106.1.82-89.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leblanc D. J., Mortlock R. P. The metabolism of D-arabinose: alternate kinases for the phosphorylation of D-ribulose in Escherichia coli and Aerobacter aerogenes. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1972 Jun;150(2):774–781. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(72)90097-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee N., Bendet I. Crystalline L-ribulokinase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1967 May 10;242(9):2043–2050. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin H. C., Lei S. P., Wilcox G. The araBAD operon of Salmonella typhimurium LT2. I. Nucleotide sequence of araB and primary structure of its product, ribulokinase. Gene. 1985;34(1):111–122. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90301-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu Z., Lin E. C. The nucleotide sequence of Escherichia coli genes for L-fucose dissimilation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jun 26;17(12):4883–4884. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.12.4883. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meinkoth J., Wahl G. Hybridization of nucleic acids immobilized on solid supports. Anal Biochem. 1984 May 1;138(2):267–284. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90808-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neuberger M. S., Hartley B. S., Walker J. E. Purification and properties of D-ribulokinase and D-xylulokinase from Klebsiella aerogenes. Biochem J. 1981 Feb 1;193(2):513–524. doi: 10.1042/bj1930513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver E. J., Bisson T. M., LeBlanc D. J., Mortlock R. P. D-Ribulose production by a mutant of Aerobacter aerogens. Anal Biochem. 1969 Feb;27(2):300–305. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(69)90036-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliver E. J., Mortlock R. P. Growth of Aerobacter aerogenes on D-arabinose: origin of the enzyme activities. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):287–292. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.287-292.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiner A. M. Genes for ribitol and D-arabitol catabolism in Escherichia coli: their loci in C strains and absence in K-12 and B strains. J Bacteriol. 1975 Aug;123(2):530–536. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.2.530-536.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. M., Stahl M. M., Kobayashi I., Stahl F. W. Improved in vitro packaging of coliphage lambda DNA: a one-strain system free from endogenous phage. Gene. 1985;38(1-3):165–175. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90215-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scangos G. A., Reiner A. M. Ribitol and D-arabitol catabolism in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1978 May;134(2):492–500. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.2.492-500.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sridhara S., Wu T. T. Purification and properties of lactaldehyde dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1969 Oct 10;244(19):5233–5238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart G. S., Lubinsky-Mink S., Jackson C. G., Cassel A., Kuhn J. pHG165: a pBR322 copy number derivative of pUC8 for cloning and expression. Plasmid. 1986 May;15(3):172–181. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(86)90035-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood W. B. Host specificity of DNA produced by Escherichia coli: bacterial mutations affecting the restriction and modification of DNA. J Mol Biol. 1966 Mar;16(1):118–133. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(66)80267-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruijn F. J., Lupski J. R. The use of transposon Tn5 mutagenesis in the rapid generation of correlated physical and genetic maps of DNA segments cloned into multicopy plasmids--a review. Gene. 1984 Feb;27(2):131–149. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90135-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]