Figure 2.
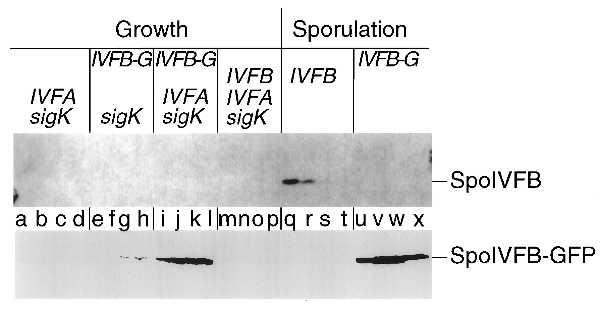
Accumulation during growth of a modified form of the putative processing enzyme SpoIVFB. A Western blot of cell extracts from B. subtilis cells is shown in which the genes or gene fusion that are listed above the blot were artificially induced during growth (lanes a–p) or were turned on in response to sporulation (lanes q–x) and analyzed with an affinity-purified antibody that recognizes the wild-type SpoIVFB protein (Upper) or a polyclonal antibody that recognizes GFP (Lower), to visualize the SpoIVFB-GFP protein fusion. The binding of the primary antibody was detected by using a chemiluminescent detection system (Upper) and a colorimetric detection system (Lower). sigK refers to the gene encoding pro-σK, IVFA refers to the gene encoding SpoIVFA, IVFB-G refers to the gene fusion encoding the SpoIVFB-GFP protein fusion, and IVFB refers to the gene encoding the wild-type SpoIVFB protein. Lowercase type (shown between the two panels) refers to the individual lanes. The lanes are divided into sets of four, with the first letter corresponding to 1 hr after induction, and each subsequent letter in the set indicating an additional hour of induction, up to 4 hr of induction (lanes a–p). Details of the induction protocol during growth and the protocol used to initiate sporulation are included in Materials and Methods. For lanes q–x, the lanes are divided into sets of four, with the first letter corresponding to the second hour of sporulation and each subsequent letter in the set indicating an additional hour of sporulation, up to the fifth hour of sporulation. Cell extracts were prepared and an amount corresponding to 0.1 ml of cells was separated by SDS/PAGE. Lanes correspond to the following strains: a–d, OR920; e–h, OR916; i–l, OR918; m–p, OR922; q–t, OR9; u–x, OR758. Note that the cell extracts used in lanes a–p are the same extracts used in Fig. 3, lanes e–p and r–u.
