Figure 4. Localization of the division inhibitor UgtP is dependent on UDP-Glc levels and FtsZ.
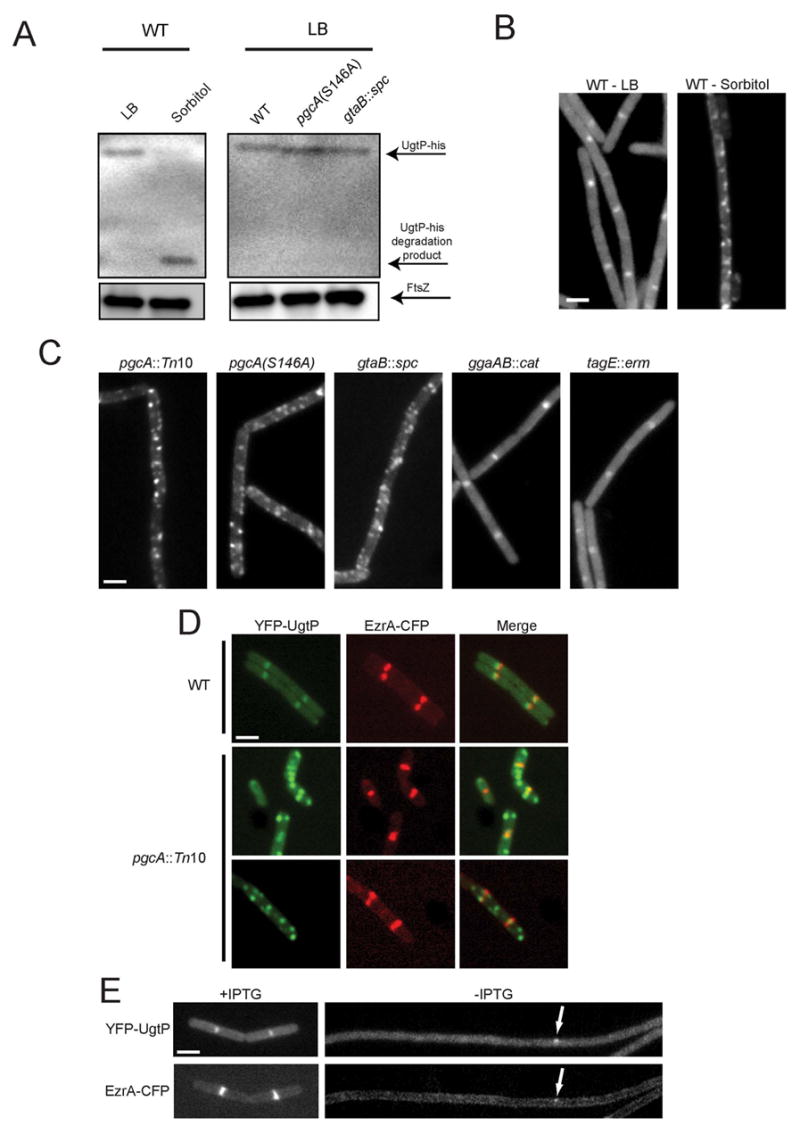
(A) Quantitative immunoblot of UgtP-his (top arrow) expressed from the native ugtP promoter. UgtP levels were ~6-fold lower in cells cultured in minimal sorbitol relative to LB (left). Middle arrow indicates UgtP degradation product in minimal sorbitol. UgtP-his levels were not decreased in pgcA(S146A) or gtaB::spc cells relative to wild type cells when grown in LB (right). FtsZ (bottom arrow) is shown as a loading standard. (B) YFP-UgtP localizes to midcell and the poles of wild type cells cultured in LB (left) but shows a punctate localization pattern and decreased cytoplasmic staining in minimal sorbitol (right). (C) YFP-UgtP localization in various strains cultured in LB. The loss of pgcA results in a punctate UgtP localization pattern similar to that observed in wild type cells cultured in minimal sorbitol. (D) Colocalization YFP-UgtP and EzrA-CFP in cells cultured in LB: YFP-UgtP (left), EzrA-CFP (middle), merged image (right). Wild type (top row), pgcA::Tn10 (bottom rows). In contrast to wild type cells, YFP-UgtP foci typically do not co-localize with EzrA-CFP in the pgcA mutants. (E) YFP-UgtP (top) and EzrA-CFP (bottom) localization in cells cultured in LB before (left) and after (right) FtsZ depletion. YFP-UgtP is diffusely cytoplasmic in the absence of FtsZ. Occasional remaining foci of YFP-UgtP (top arrow) correspond to remaining foci of EzrA-CFP (bottom arrow). Bars = 2 μm.
