Figure 3.
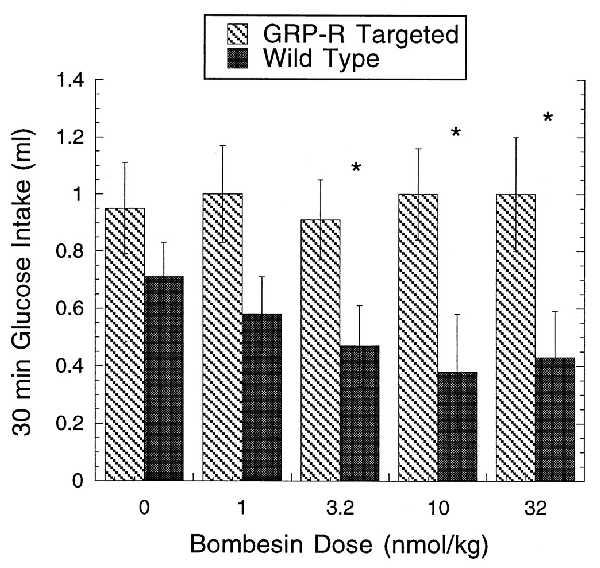
Effect of BN on glucose uptake. Thirty-minute glucose intake in GRP-R-targeted (−/Y) male mice and wild-type (+/Y) male littermates after intraperitoneal administration of BN at 0 (0.9% saline) or 1.0, 3.2, 10, and 32 nmol/kg. BN produced a significant suppression of glucose intake in wild-type mice at doses of 3.2, 10, and 32 nmol/kg but failed to suppress intake at any dose in GRP-R-targeted mice. ∗, Significantly different from 0.9% saline (P < 0.05).
