Figure 4.
Analysis of ESD4 Function in Vitro and in Vivo.
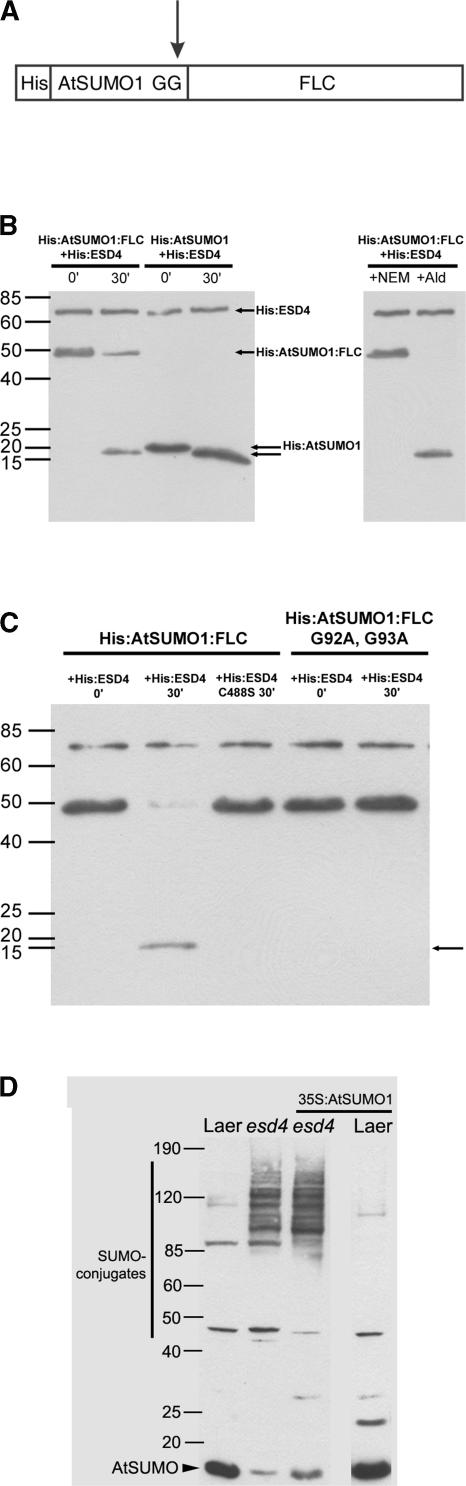
(A) Diagram of the synthetic AtSUMO1 precursor (HIS:AtSUMO1:FLC) used in the in vitro experiments. Ten HIS residues are fused at the N terminus of AtSUMO, and the FLC protein is fused at the C terminus. The arrow indicates that SUMO-specific protease is expected to cleave immediately after two highly conserved Gly residues (Figure 3). FLC is present only to increase the size difference between the precursor and the mature protein.
(B) Cleavage of HIS:AtSUMO1:FLC by HIS:ESD4 in vitro as analyzed on a protein gel blot probed with antibody against the HIS epitope tag. The gel at left shows the results of incubating HIS:ESD4 with either HIS:AtSUMO1:FLC or HIS:AtSUMO1 for 0 or 30 min at 37°C. The bottom, unlabeled arrow indicates the novel product of the reactions incubated for 30 min and is the size expected for mature HIS:AtSUMO1. The gel at right shows the effects of incubating HIS:ESD4 with HIS:AtSUMO1:FLC for 30 min at 37°C in the presence of the ubiquitin inhibitor aldehyde (Ald) or 5 mM N-ethylmaleimide (NEM). N-Ethylmaleimide prevents the appearance of mature SUMO and therefore inhibits the reaction, whereas aldehyde does not.
(C) Effect of amino acid substitutions in HIS:ESD4 or HIS:AtSUMO1:FLC. Lanes 1 and 2 show both wild-type proteins incubated for 0 or 30 min. Lane 3, HIS:ESD4(C488S) incubated with HIS:AtSUMO1:FLC for 30 min. Lanes 4 and 5, HIS:AtSUMO1:FLC(G92A G93A) incubated with HIS:ESD4 for 0 or 30 min. Both mutations prevent the production of mature HIS:AtSUMO.
(D) SUMO conjugate patterns in wild-type, esd4, and transgenic Arabidopsis plants. From left to right: Ler, esd4-1, transgenic esd4-1 overexpressing mature AtSUMO1, and transgenic Ler overexpressing mature AtSUMO1. Total proteins were transferred to a filter and probed with AtSUMO1 antibody. Similar results were obtained from plants overexpressing mature AtSUMO2 or mature AtSUMO3 and from plants overexpressing the precursors of AtSUMO1, AtSUMO2, or AtSUMO3.