Figure 1.
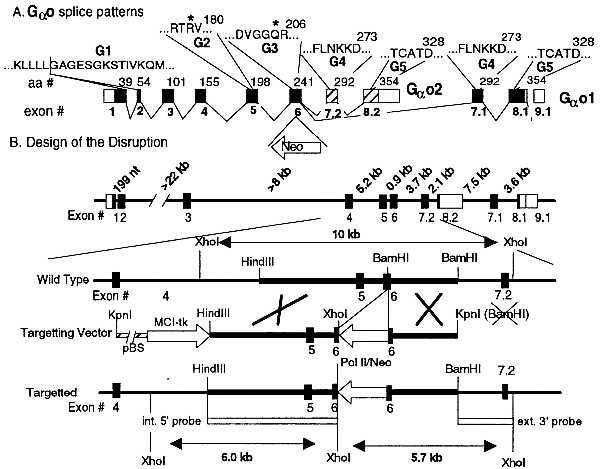
Genomic organization of the gene encoding Go α subunits and design of the disruption. (A) Intron–exon boundaries of the cDNA coding for Goα and location of key amino acid sequences. Boxes, exons; open boxes, untranslated sequences; solid or hatched boxes, translated sequences. Exon numbering is shown below and the number of the last amino acid of each exon is shown above the cDNA. Amino acids in G1 through G5 regions are responsible for binding and hydrolysis of GTP (31). Mutations in R* and Q* of G2 and G3 reduce GTPase activity (32). Pertussis toxin (PTX) ADP ribosylates a Cys at position −4 from C terminus. (B) Genomic structure of the Goα gene (29, 30), structure of the targeting vector, 3′ and 5′ probes for Southern blot analysis, and expected restriction fragment sizes of the wild-type and the mutated alleles.
