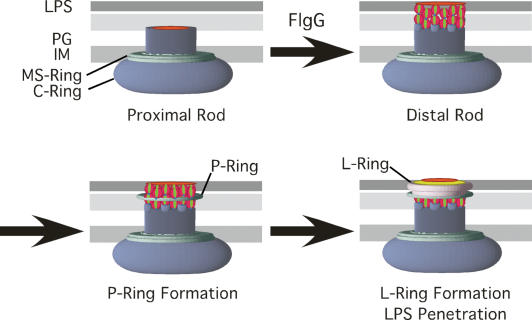
Figure 6.
A model of a checkpoint in flagellum assembly. A FlgG stop-polymerization signal couples rod completion to P- and L-ring assembly and outer membrane penetration of the growing flagellum. Two stacks of FlgG subunits polymerize onto the proximal rod to complete the rod structure. A P-ring forms around two layers of FlgG subunits. This is followed by L-ring formation on the P-ring and within the outer membrane, which effectively opens a hole in the outer membrane to allow polymerization of the flagellum outside the cell. (IM) Inner membrane; (PG) peptidoglycan; (LPS) lipopolysaccharide.