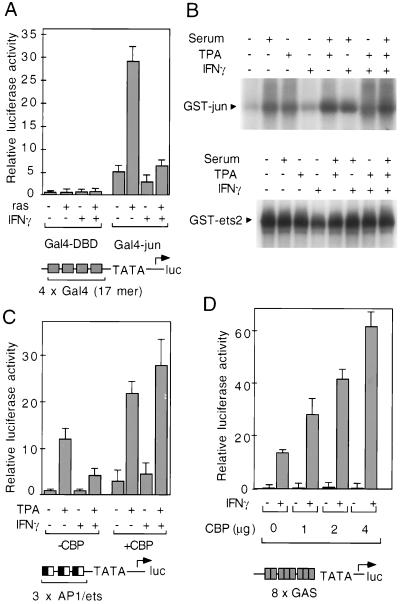
Figure 2.
IFN-γ inhibits the transcriptional activities of AP-1 and cooperating ets factors. (A) IFN-γ inhibits the activities of the c-jun transactivation domain. The N-terminal transactivation domain of c-jun was fused in frame to the GAL4 DNA binding domain and used to direct expression of a Gal4-dependent promoter. Transactivation domain function was stimulated by cotransfection of a Val-12 Ras expression plasmid. (B) Effects of IFN-γ on c-Jun kinase and ets2 kinase activities. HeLa cells were rendered quiescent by culture in serum-free media for 16 hr and then treated with IFN-γ, TPA, and/or serum as indicated. Cell lysates were then assayed for Jun N-terminal kinase and ets2 kinase activities (24). (C) Overexpression of CBP relieves IFN-γ antagonism of AP-1/ets activities. The 3× AP-1/ets-promoter was cotransfected into THP-1 cells with 1 μg of a CBP expression plasmid or an equivalent amount of empty expression plasmid and treated with IFN-γ and/or TPA. (D) Overexpression of CBP potentiates transcriptional responses to IFN-γ. A luciferase reporter gene containing eight GASs linked to a minimal prolactin promoter was cotransfected into HeLa cells with increasing amounts of a vector directing expression of CBP (24). Error bars for A, C, and D are standard deviations.