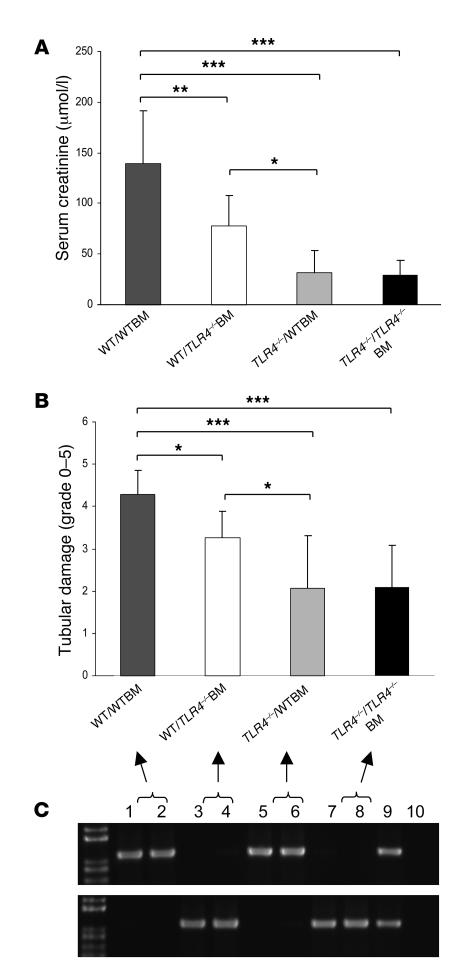
Figure 13. Functional TLR4 on intrinsic kidney cells makes the more significant contribution to kidney damage.
WT/WTBM mice showed significant kidney dysfunction and injury at day 1 after ischemia/reperfusion, while TLR4–/–/TLR4–/–BM chimeric mice were protected from kidney IRI as measured by day 1 serum creatinine (A) and tubular damage (B). Creatinine levels and tubular injury scores replicated those observed in WT and TLR4–/– mice (Figures 5 and 6), excluding an effect of the BM transplant procedure per se on the response to renal ischemia. Moreover, TLR4–/–/WTBM chimeras were protected from kidney IRI to the same degree as TLR4–/–/TLR4–/–BM mice, while WT/TLR4–/–BM mice enjoyed only partial protection as assessed by day 1 serum creatinine and tubular damage (A and B). Data shown are mean ± SD. n = 7–10 per group. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001. Full replacement of hematopoietic cells in the chimeric mice was confirmed by genotyping of genomic DNA from whole blood using PCR. PCR products shown on representative gels (C). The top panel represents PCR products for the WT allele DNA, and the bottom panel represents PCR products for the mutated allele DNA (lanes 1–2: WT/WTBM; lanes 3–4: WT/TLR4–/–BM; lanes 5–6: TLR4–/–/WTBM; lanes 7–8: TLR4–/–/ TLR4–/–BM; lane 9: TLR4 heterozygous blood as positive controls; and lane 10: negative controls).