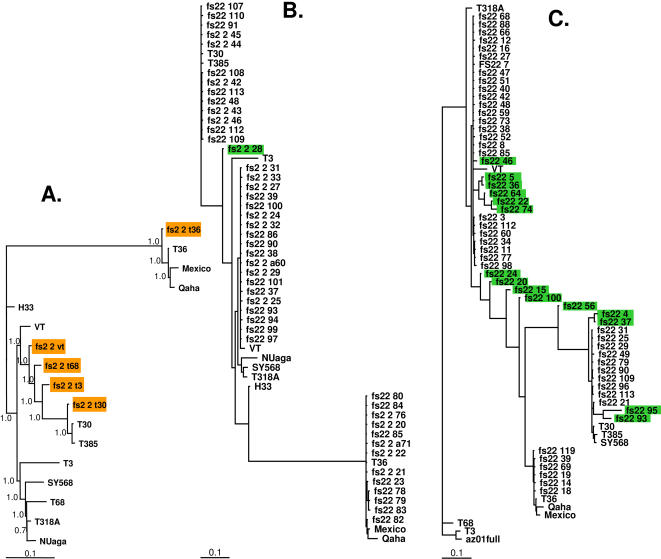
Figure 3. Bayesian phylogenetic inference of CTV genomes and genome fragments.
Unrooted, consensus phylogenetic trees were obtained from 2,000,000 generations of the Markov chain Monte Carlo simulation in Bayesian analysis using a general time-reversal model of nucleotide substitution [33]. The number above each branch indicates the Bayesian posterior probability. The scale bars represent 0.1 expected substitutions per site. Branch lengths are proportional to evolutionary distance. Sequences were aligned using ClustalX [47] and subsequently manually aligned prior to the Bayesian phylogenetic analysis. A, Known CTV genomes and CTV genomes assembled from resequencing analysis of FS2-2 (highlighted orange). The suffix at the end of fs2_2 distinguishes multiple genotypes in the isolate and also indicates the anchor sequence from which the consensus contig was generated by the Phrap program. B, the 5′ proximal 1 kb, and C, p33-coding region of CTV genomes obtained by direct sequencing of RT-PCR clones. In both B and C, Bayesian posterior probability and clones with identical sequences were omitted for clarity. Recombinant sequences are highlighted in green.