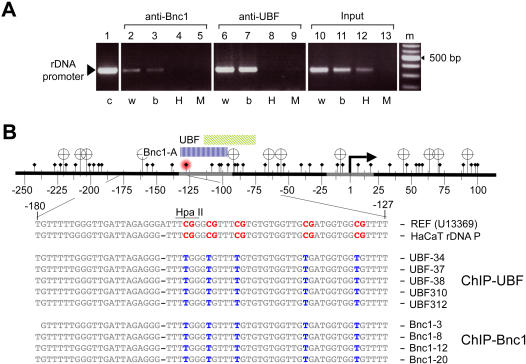
Figure 4. Basonuclin-associated rDNA promoter is hypomethylated.
The DNA methylation status of basonuclin-associated rDNA promoter was analyzed by the HpaII/MspI sensitivity assay (A) and by bisulfite sequencing (B). A, A PCR analysis of the integrity of the rDNA promoter after HpaII or MspI digestion. The source of PCR templates is indicated above the gel image, and the treatment received by the templates, below. c, control template (genomic DNA), w, templates were incubated in water, b, in restriction buffer, H, with HpaII, M, with MspI. B, Depicted on top is the region of rDNA amplified by the PCR shown in A. Transcription start site is indicated as a bent arrow and the cis-elements are depicted as gray segments. HpaII/MspI sites are shown as banners and CpG sites, diamond-headed pins. Cytosine at position −132 is marked with a red hallo. The regions of basonuclin and UBF DNase I footprints are indicated by color-coded bars above the DNA. Listed below are DNA sequences from the region in between −180 to −126. The reference (U13369) and HaCaT rDNA promoter consensus sequences (the first two lines, respectively) are shown as they are sequenced after bisulfite treatment; i.e., all CpGs (in red) are assumed to be methylated and the rest of the Cs are converted to Ts due to the bisulfite treatment. The rest nine sequences are actual bisulfite sequencing data from five UBF-associated promoters and four basonuclin-associated promoters. The presence of a T (in blue) in the CpG position signifies that the CpG was not methylated.