FIG. 4.
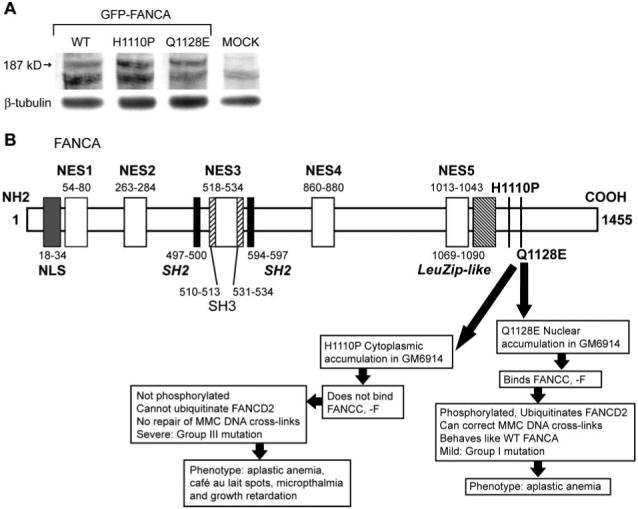
Expression analysis and schematic of FANCA point mutations. A, Western blotting analysis of protein extracts made from untransfected (MOCK) and cells transfected with GFP-tagged WT and mutant (H1110P and Q1128E) proteins identified a 187-kDa GFP-FANCA fusion protein. Blots were stripped and reprobed with β-tubulin to control for protein loading. B, Schematic representation of WT and the two mutant forms of FANCA. WT FANCA is 1455 amino acids with a NLS at the NH2-terminus (15) and five nuclear export signals (NES) (36). Putative domains include Src-homology domains (SH2, SH3) and a leucine zipper-like motif (LeuZip-like) and are shown in italics (13). The biochemical properties and phenotype of the point mutations H1110P and Q1128E are also summarized (14, 25, 27). The numbers orientate the domains on the amino acid backbone. MMC refers to ability of FANCA to repair DNA cross-links generated by mitomycin C.
