Figure 2. PU.1 expression is reduced by the BN mutation in both myeloid and lymphoid lineages.
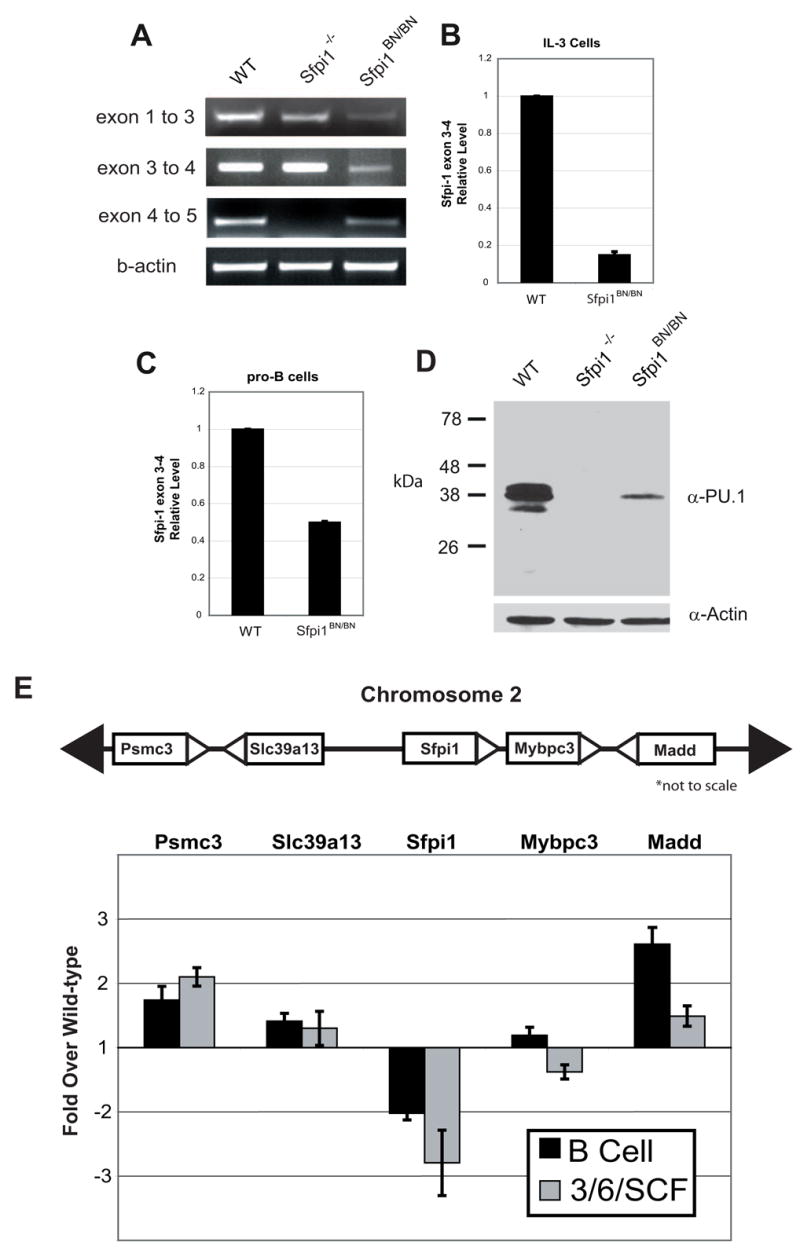
(A) RT-PCR analysis of transcription across the Sfpi1 locus. PCR was performed using primers that reside within the exons indicated. The lack of product between exons 4 and 5 in the Sfpi1−/− cells is due to the partial deletion of exon 5 [4]. (B, C) Real-time RT-PCR was used to measure Sfpi1 exon 3 to 4 transcripts in cultured IL-3 cells (B) or cultured IL-7 and stromal cell pro-B cells (C) from wild-type or Sfpi1BN/BN fetal liver. (D) Western blot for PU.1 protein expression in nuclear lysates of pro-B cells of the indicated genotype. Quantitative analysis demonstrated a 5-fold reduction in PU.1 expression. (E) Real-time RT-PCR analysis of RNA transcripts from pro-B cells or fetal liver progenitors cultured for 2 days in IL-3, IL-6, and SCF. Bars indicate the fold change in transcriptional expression in Sfpi1BN/BN cells compared to wild-type cells using primers that recognize the genes indicated. Gene location in relation to Sfpi1 is shown above. Error bars indicate the standard error.
