Fig. 2.
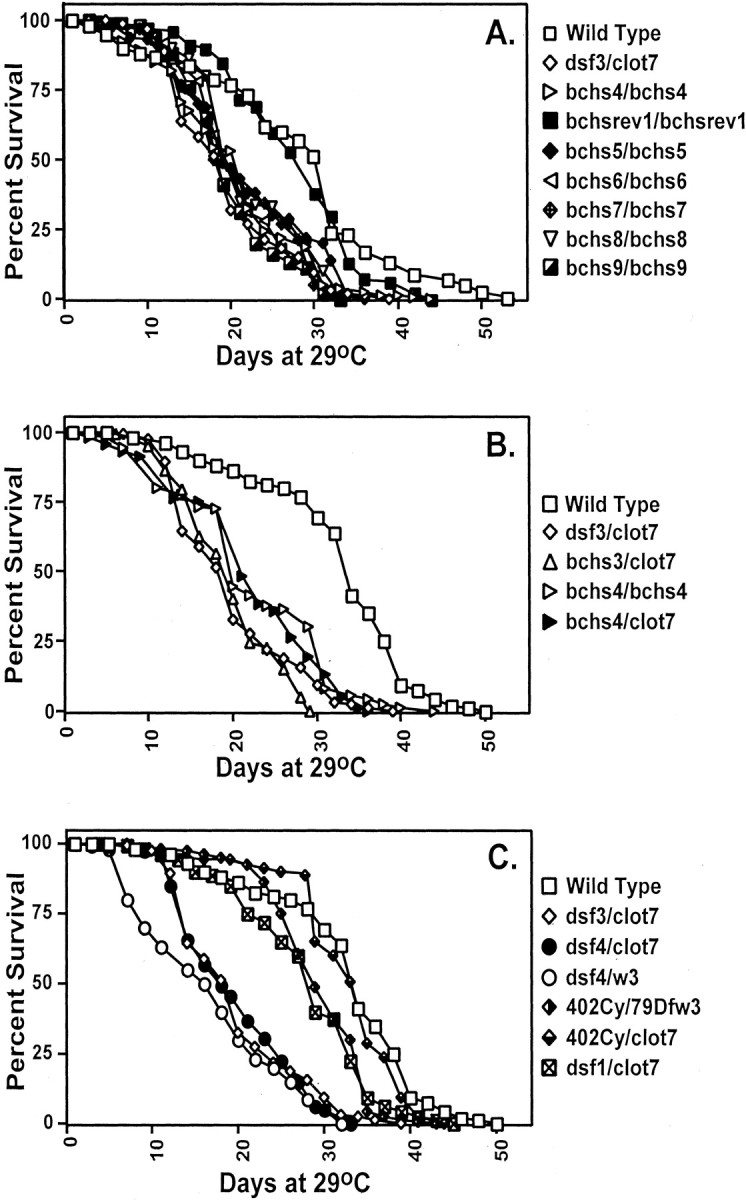
Premature death of bchs mutants. Newly eclosed males were collected and aged at 29°C for the duration of the experiments. A, Imprecise excisions of thebchs4 P-element, generating alterations in the 5′ region of the bchs gene, result in a shortened average life span, as shown by thebchs5/bchs5,bchs6/bchs6,bchs7/bchs7,bchs8/bchs8, andbchs9/bchs9fly lines. Rescue of premature death occurs when the samebchs4 P-element is removed precisely from its bchs location, as demonstrated by thebchsrev1/bchsrev1line. B, P-element insertions in the first intron ofbchs reduce average life span, as seen inbchs3/Df(2L)clot7,bchs4/bchs4, and bchs4/Df(2L)clot7 genetic combinations. C, Flies containing one or more wild-type copies of bchs, Canton S, 402Cy/Df(2L)w3, or 402Cy/Df(2L)clot7 have an average life span between 29.0 and 32.5 d. Adults with both copies of the bchs genomic region removed, Df(2L)dsf3/Df(2L)clot7, Df(2L)dsf4/Df(2L)w3, or Df(2L)dsf4/Df(2L)clot7 flies, show a 40–45% reduction in average life span when compared with controls. Mutating the dsf gene in the case of dsf1/Df(2L)clot7 flies does not alter average adult longevity significantly. Mean lifespan, SDs, and p values for a selection of genotypes are summarized in Table 1.
