Fig. 3.
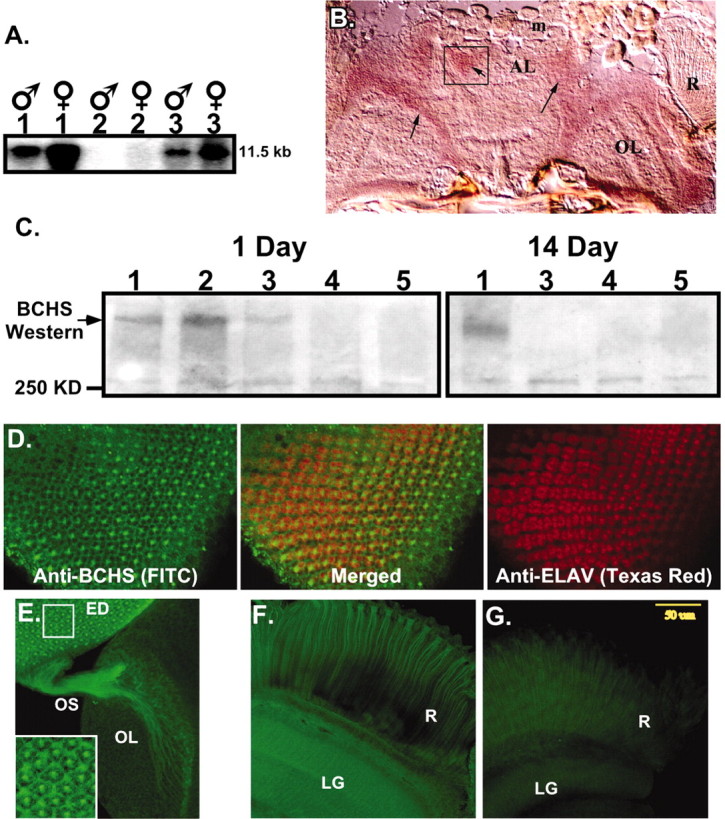
BCHS mRNA and protein expression patterns.A, Northern blot analysis of total RNA from 20 adult male and female heads. Wild-type (1) anddsf1/Df(2L)clot7 (3) mutant brains express a single, nearly 12.0 kb mRNA that is absent from Df(2L)dsf3/Df(2L)clot7 flies (2). B, Frozen sections from wild-type pharate adults (Finley et al., 1998) were used for in situ hybridization to bchs mRNA. Specific labeling for bchs is detected in a horizontal section through the head at the level of the antennal lobes. Labeling is seen in cortical regions containing neuronal cell bodies and is absent from neuropil areas. Arrows point to labeled cortical cells; the antenna lobe (AL), optic lobe (OL), and retina (R) are indicated. mRNA was not detected in muscles of the head (m) or other tissues. Sections through adult thorax also show uniformbchs labeling in thoracic and abdominal ganglia neurons and not in other tissues (data not shown). C, Western blot analysis of BCHS shows a protein running well above the largest molecular weight marker (250 kDa) in head extracts from 1-d-oldCanton S (1) and 402CyO/Df(2L)clot7 (2) wild-type controls. At this age bchs4/Df(2L)clot7 flies (3) express some BCHS, whereas BCHS is absent from bchs3/Df(2L)clot7 (4) and Df(2L)dsf3/Df(2L)clot7 (5) flies. At 2 weeks only wild-type flies (1) have detectable levels of the BCHS protein. Protein no longer is detected inbchs4/Df(2L)clot7 flies (3). D–F, Subcellular location of the BCHS protein. D, Immunofluorescence staining of a third instar larval eye disc double-labeled for BCHS (basal section;FITC) and neuronal-specific marker ELAV (apical section;Texas Red). The two proteins demonstrate similar temporal expression patterns in neurons, but ELAV is located primarily within the nucleus while BCHS is found in cytoplasm (center; merged panel).E, Eye disc (ED), optic stalk (OS), and attached larval optic lobe (OL) are stained for BCHS (FITC). The protein is found along the entire length of photoreceptor axons. The inset is an enhanced intensity image showing BCHS extending as far as growth cones. This pattern is visible only because of the lack of BCHS expression in surrounding undifferentiated neuroblasts at this developmental time point. F, Mature BCHS expression pattern in a retina (R) and laminal ganglion (LG) optical section of a 2-week-olddsf1/Df(2L)clot7 adult (n = 9). BCHS protein levels are still high in older adults (consistent with Western blots). The protein remains located in the cytoplasm of retinal axons and in laminal ganglia.G, Enhanced image of an identically prepared retina and attached CNS from an age-matched bchs mutant [Df(2L)dsf3/Df(2L)clot7; n = 11]. This level of staining is similar to secondary antibody alone and is substantially below the staining of bchs+animals.
