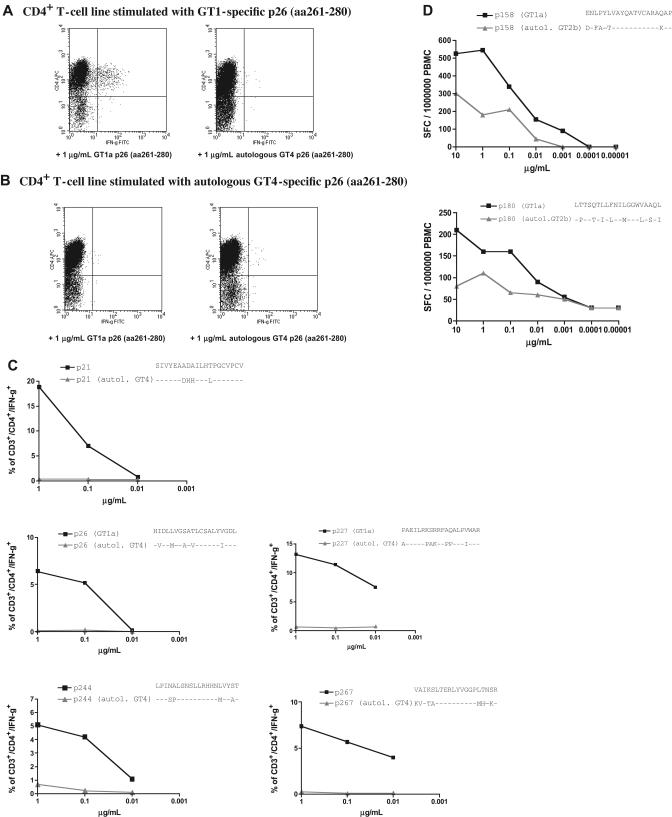
Figure 7.
HCV GT1a-based peptides, but not peptides representing autologous sequence, are recognized in patients infected with non-GT1 strains. Strong and durable responses against 5 different GT1a-based HCV peptides were detected in patient C29 (Figure 3). This patient was infected with GT4 virus and showed a serologic response to GT1 virus. We were able to cultivate peptide-specific lines (A) by stimulating with GT1-based peptides, but not with autologous peptides (B) (“Patients, materials, and methods”). (C) dilution ICS assays performed on GT1-specific CD4+ T-cell lines for all specificities confirm the lack of recognition of peptides representing the autologous sequence of patient C29 (“Patients, materials, and methods”) (D) Ex vivo dilution ELISPOT data for 2 strong responses against p158 (1581-1600) and p180 (1801-1820) confirm that peptides based on GT1a sequence (■) elicited much higher responses than peptides based on autologous GT2b sequence (▲) in patient non-GT1 C35 (“Patients, materials, and methods”).