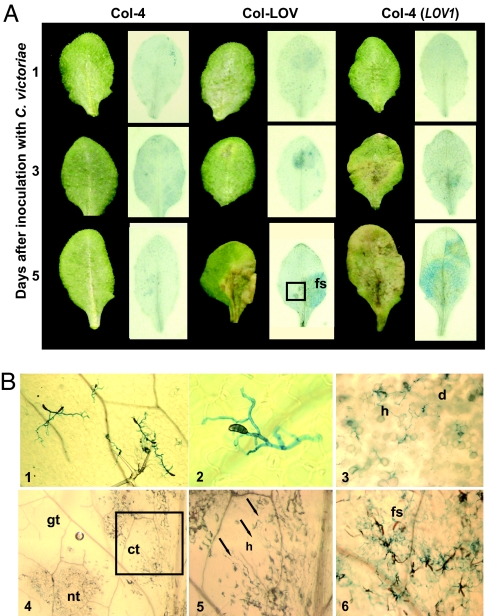
Fig. 4.
Genotype-specific symptom development and C. victoriae ingress in A. thaliana. (A) Leaves of C. victoriae-resistant (Col-4) and C. victoriae-susceptible [Col-LOV and Col-4 (LOV1) transgenic] plants days after inoculation with 10 μl of 1 × 105/ml C. victoriae spores are shown before (Left) and after (Right) staining with trypan blue. Dead and dying cells appear blue-black and fungal hyphae appear bright blue. (B) Select leaves from A, depicted with Nomarski (panels 1–3 and 6) or stereoscope (panels 4 and 5) microscopy; Col-4, 5 days after inoculation, panel 1 (magnification: ×40), and 2 (magnification: ×400); Col-LOV, at 3 days, panel 3 (magnification: ×100); and 5 days after inoculation, panel 4 (magnification: ×25), panel 5 (magnification: ×63), and panel 6 (magnification: ×80). The boxed region of the Col-LOV leaf at 5 days after inoculation in A, contains green, chlorotic, and necrotic tissues and is shown at 25× magnification (4). A higher magnification of the boxed region in 4 is shown in 5. Arrows point to hyphae in chlorotic tissue. Hyphae are abundant and sporulation is occurring from the same leaf, to the right of the midvein (6). fs, fungal sporulation; h, hyphae; d, dead or dying cells; gt, green tissue; ct, chlorotic tissue; nt, necrotic tissue.