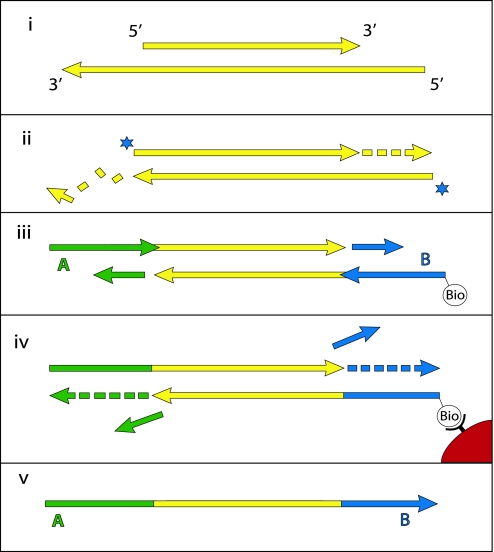
Fig. 1.
The 454 library preparation process. Double-stranded DNA molecules (i) (yellow) are made blunt-ended by T4 DNA polymerase, 5′-phosphorylated (stars) by T4 polynucleotide kinase (ii) and ligated to one strand of nonphosphorylated double-stranded adaptors A (green) and B (blue) (iii). Ligation products carrying the biotinylated B adaptor are captured on Streptavidin beads (red), and the strand-displacing Bst DNA polymerase is used to extend the nicks between adaptors and template (iv). The DNA strands are then denatured, releasing the A-to-B strands (v), which are isolated and used as templates for emulsion PCR.