Fig. 1.
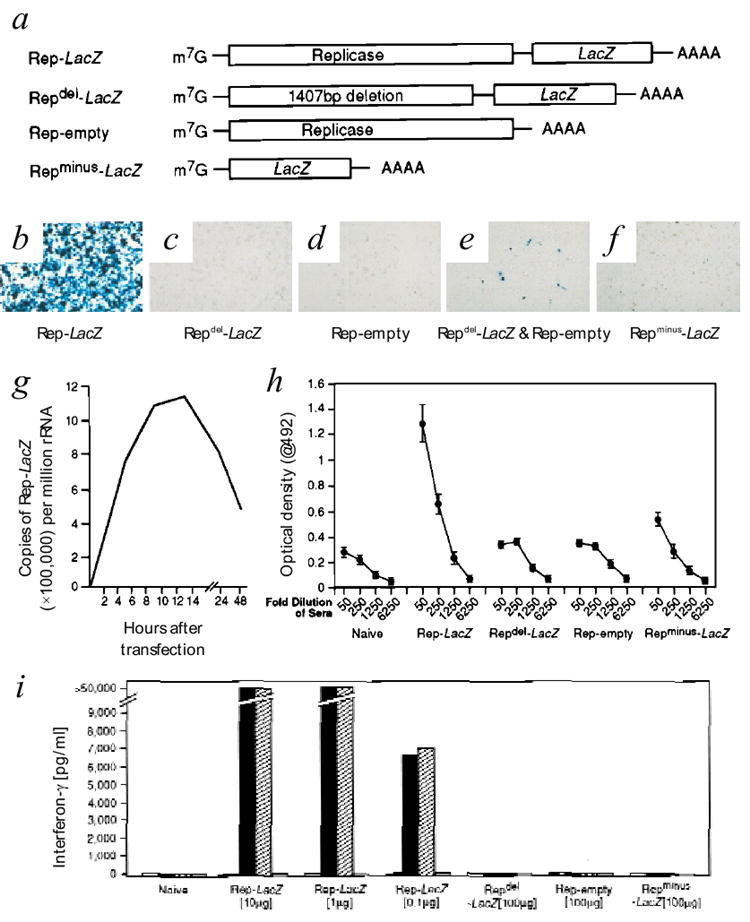
Structure, function and immunogenicity of self-replicating RNA vaccines. a, RNA constructs used for immunization. m7G, ‘cap’ at the 5′ end of the mRNA. b–f, RNA constructs transcribed and capped in vitro were transfected into BHK21 cells; 24 h later, cells were tested for β-gal expression using the X-gal assay. Data are representative of three independent experiments with similar results. g, Quantitative analysis of RNA replication using TaqMan real-time RT–PCR. Total cellular RNA was isolated at 6, 10, 14, 24 and 48 h after transfection with the Rep-LacZ RNA. Using vector-specific primers, the copy number of the mRNA Rep-LacZ was then quantified relative to 18s ribosomal RNA. This experiment was done three independent times with similar results. h, Induction of antigen-specific antibody responses in mice by self-replicating RNA vaccines. Sera obtained from mice 21 d after immunization with RNA were tested by ELISA for the presence of IgG antibodies against the recombinant β-gal protein. i, Induction of CD8+ T-cell responses in mice by self-replicating RNA vaccines. Splenocytes obtained from mice 21 d after immunization with RNA were re-stimulated in vitro in the presence of β-gal876-884, then cultures were assayed for β-gal-specific CD8+ T-cell recognition by measuring IFN-γ release after exposure to CT26 alone (□) or pulsed with the synthetic peptides derived from β-gal876-884 (▨) or P815A35-43 (
 ) or transduced with a retrovirus encoding LacZ (■).
) or transduced with a retrovirus encoding LacZ (■).
