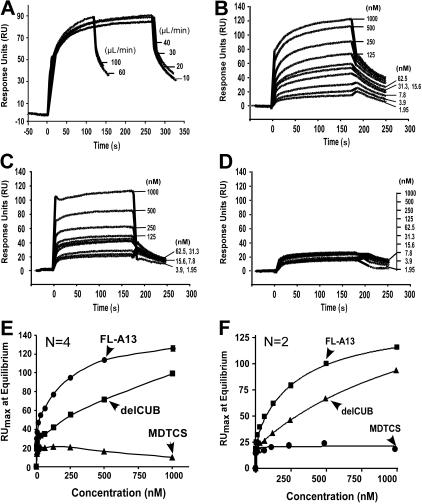
Figure 3.
Kinetic binding interaction between VWF and ADAMTS13 (or variants) under flow. (A) Effect of flow rates on binding of VWF to ADAMTS13. Purified VWF (18.75 μg/mL or 50 nM) was injected at various flow rates for 3 to 5 minutes over the CM5 surface immobilized with FL-A13 in absence of EDTA. (B-D) Binding of VWF to ADAMTS13 and C-terminal truncated variants. Purified VWF at various concentrations (0 to 250 μg/mL or 0 to 1000 nM) was injected over the surfaces immobilized by FL-A13 (B), delCUB (C), and MDTCS (D). After equilibrium was established, the HBS-T buffer was then injected over the surface to allow the dissociation to occur. The representative sensograms in absence of EDTA are shown in panel A-D. The maximal response units (RUmax) at equilibrium (y-axis) were obtained from the sensograms and plotted against various concentrations of VWF injected (x-axis). The entries in panels E and F are the mean of 2 to 4 repeats in absence (E) or presence (F) of 10 mM EDTA. The equilibrium dissociation constant, KD, was calculated by fitting the data to the binding isotherm using nonlinear regression.