Fig. 3. Identification of glycoconjugate-bound O-acetyl sialic acid derivatives in human tear fluid by fluorometric HPLC.
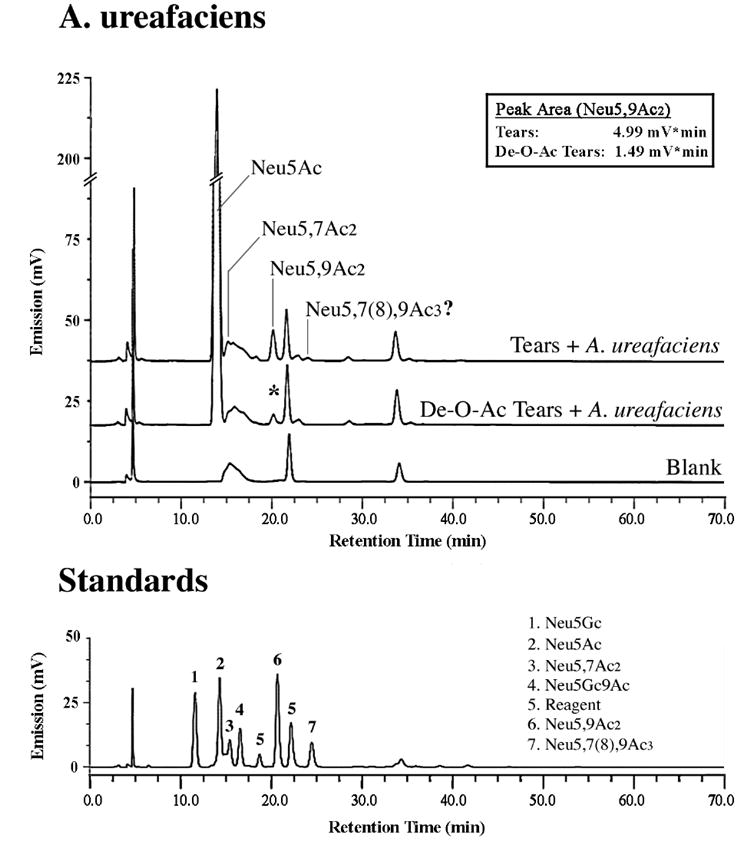
Sialic acids were hydrolyzed using sialidase from A. ureafaciens. In addition to a major peak corresponding to Neu5Ac, two peaks corresponding to Neu5,7Ac2 and Neu5,9Ac2 were identified by fluorometric HPLC and confirmed by tandem HPLC-electrospray MS (see Results). An additional peak, with a retention time similar to that of the Neu5,7(8),9Ac3 standard, was detected by fluorometric HPLC but not by electrospray MS. De-O-acetylation of the sample by alkaline hydrolysis reduced the peak area of Neu5,9Ac2, which correlates with a diminution in H185 binding after alkaline hydrolysis (Fig. 2). The profile of sialic acids is shown relative to standard sialic acids (bottom).
