Fig. 5. Relative abundance of sialic acid derivatives isolated from human tear fluid.
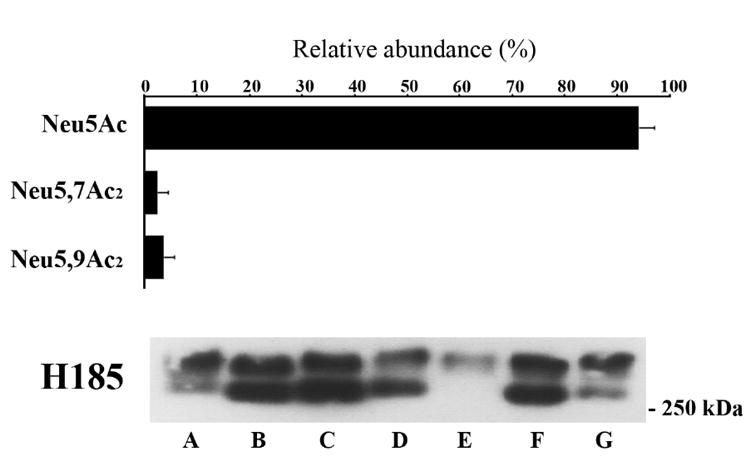
Seven human tear samples were hydrolyzed using sialidase from A. ureafaciens and individually analyzed by fluorometric HPLC. Shown is the relative abundance of individual sialic acids as a percentage of total sialic acid (values are mean ± SD, n=7). The presence of the H185 carbohydrate epitope in each sample (A-G) analyzed by fluorometric HPLC is confirmed by western blot (5-50 μg of total protein). The presence of two molecular weight bands migrating over 250 kDa may result from mucin polymorphism (individual mucin alleles are expressed co-dominantly), or the presence of different mucin gene products or glycoforms containing the H185 carbohydrate epitope in the sample.
