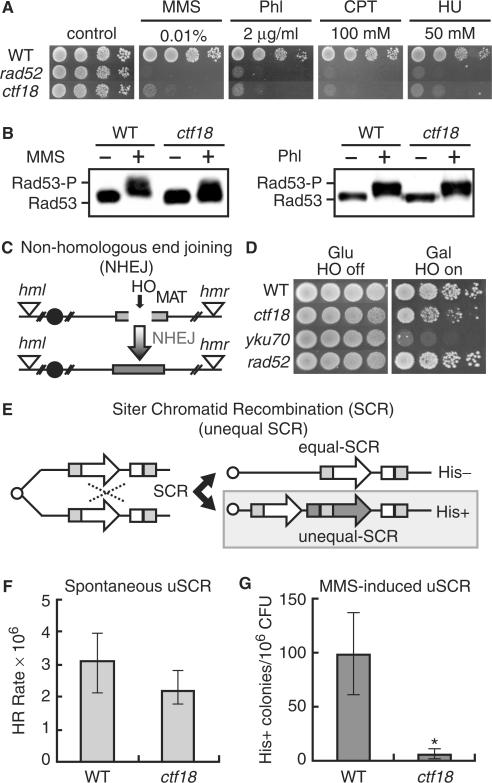
Figure 1.
Ctf18 is involved in DSB repair by HR, but not in NHEJ. (A) Sensitivity to various DNA-damaging agents. Wild-type (SCRL), rad52 (YHO602) and ctf18 (YHO605) cells were inoculated on YPAD plates containing the indicated concentrations of methyl methanesulfonate (MMS), phleomycin, camptothecin or hydroxyurea (HU). The plates were incubated for 3 days at 30°C and then photographed. (B) Modification of Rad53 in response to DNA damage. Wild-type (YHO302) and ctf18 (YHO308) cells expressing Rad53-13Myc were arrested in G2/M phase and then exposed to 0.1% MMS or 100 μg/ml phleomycin for 2 h at 30°C. Aliquots of the cultures were taken before (−) and after (+) exposure to MMS or phleomycin for 2 h. Proteins prepared from these cells were subjected to SDS-PAGE. The Rad53 protein was detected by western blotting using an anti-Myc antibody. (C) Schematic representation of the process and outcome of NHEJ at the galactose-inducible HO endonuclease-specific DSB site on chromosome III in yeast strain JKM179. (D) The NHEJ DSB repair pathway is intact in ctf18 mutants. The viability of wild-type (JKM179), yku70 (YHO505), rad52 (YHO506) and ctf18 (YHO511) mutants on a background of an HR-repair defective yeast strain was determined by growing the cells on either glucose (HO off) or galactose (HO on). A galactose-inducible HO endonuclease was integrated at the ADE3 locus of a haploid yeast strain that was defective in HR-mediated DSB repair. Upon switching the cells to galactose, the HO endonuclease is expressed that induces a single DSB at the MATα locus. Functional DSB repair can occur only through the NHEJ pathway in this strain, since the HM donor loci, HML and HMR, are deleted. (E) A schematic representation of the process and outcome of unequal sister chromatid (USCR) recombination. (F) Spontaneous unequal sister chromatid recombination rates. Wild-type (SCRL) and ctf18 (YHO605) cells were inoculated onto YPAD plates or SC plates lacking His and then incubated at 30°C for 3 days. Spontaneous unequal sister chromatid recombination rates were determined by the median method (34,35). The average number of viable cells (CFU) in the twelve independent colonies and the median number of His+ colonies for all twelve independent colonies was determined after incubation at 30°C for 3 days. The rate of production of recombinants was then calculated by the method of the median HR rates (34,35). The data present the mean and confidential interval (95%<) is shown and (G) MMS-induced sister chromatid recombination (SCR). Wild-type (SCRL) and ctf18 (YHO605) cells were inoculated onto YPAD plates or SC plates lacking His with 0.008% MMS and then incubated at 30°C for 3 days. The viability of the cells cultured with 0.008% MMS was 98%, and 34% for wild type (SCRL) and ctf18 (YHO605), respectively. The frequency of SCR is presented as the number of His colonies per 106 colony forming units (CFU). The columns and error bars represent the means and SDs of eight samples. Statistical difference in the recombination frequency was evaluated between WT and ctf18 mutant cells by Student's t-test (P < 0.001).