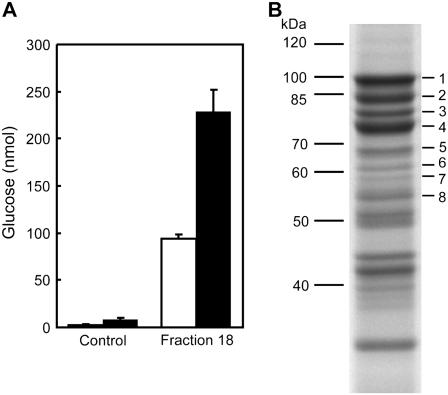
Figure 1.
Breakdown of granular starch by Arabidopsis proteins is stimulated by simultaneous glucan phosphorylation. A, Starch degrading activity of the protein fraction obtained from Arabidopsis leaves using four purification steps. Sex1-3 starch granules (2.5 mg) were incubated with 60 μL fraction 18 (MonoQ) or 60 μL buffer (control) with (black bars) or without (white bars) 0.5 mm ATP in the presence of 1.6 μg recombinant potato GWD. Final volume of the assay: 120 μL. Following incubation at 25°C for 90 min the starch was sedimented by centrifugation. Starch breakdown products present in the supernatant were hydrolyzed with acid and subsequently Glc was quantified. The slightly increased Glc content in the ATP-containing control was not consistently observed in independent experiments. B, SDS-PAGE of fraction 18 and protein identification using MALDI-MS. Proteins were separated by SDS-PAGE (10% acrylamide in the separation gel). Following staining with Coomassie Blue bands were excized, digested with trypsin, and the peptides were analyzed by MALDI-MS and database search. The following proteins were identified: 1, 2, 3 = SBE3 (At2g36390); 4 = ISA3 (At4g09020) + SBE3; 5 = putative Phosphatase (At3g01510); 6 = unknown protein (At3g55760); 7 = BAM1 (At3g23920); 8 = DPE1 (At5g64860). Proteins ≤55 kD were also analyzed but were not related to carbohydrate metabolism.