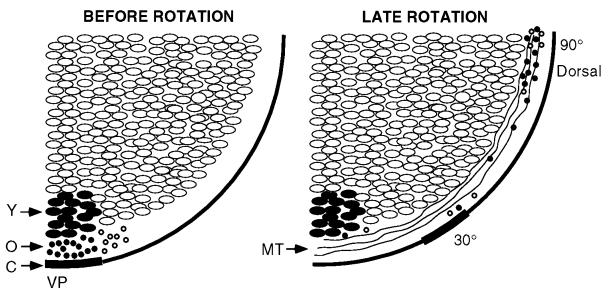
Figure 5.
Model of microtubule-mediated rapid transport of dorsalizing components in a free-floating (nonimmobilized) egg. (Left) The highlighted region at the vegetal pole represents a spot [labeled with nile red and DiOC6(3)] before cortical rotation [Y, yolk platelets; O, small organelles (•, labeled; ○, unlabeled); C, cortex; VP, vegetal pole]. (Right) The location of various components near the end of rotation are shown on the right (MT, microtubules). The core of yolk platelets remains oriented downward, the cortex moves ≈30° along the microtubules, and some organelles in the microtubule transport zone (4–8 μm from the cell surface) move ≈90° along microtubules to the equatorial region on the future dorsal side of the embryo.