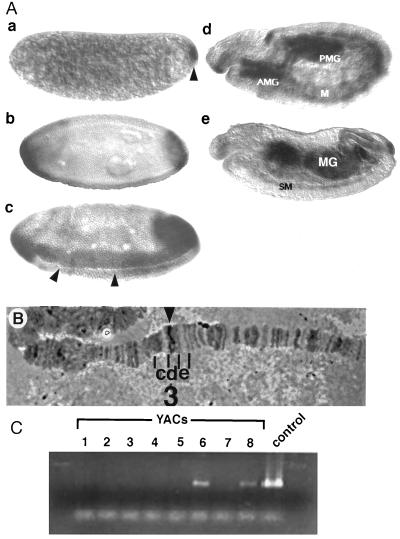
Figure 3.
(A) Spatial pattern of dmyc1 transcript distribution during embryogenesis. Side views of whole-mount embryos with anterior to the left and dorsal up × 80. Embryo a, cleavage stage. dmyc1 RNA is concentrated in the pole plasm at the posterior pole (arrowhead); a low level of uniform expression is detected throughout the rest of the embryo. Embryo b, cellular blastoderm stage before the onset of gastrulation. dmyc1 exhibits two caps of expression at the poles of the embryo. The initiation of expression along the ventral surface also can be detected. Embryo c, gastrulation stage. Expression is seen in the anlagen of the anterior and posterior midgut at the poles and in the mesoderm flanking the invaginating ventral furrow (arrowheads). Embryo d, germ-band-extension. dmyc1 RNA is detected in the invaginated anterior midgut (AMG) and posterior midgut (PMG), and in tissues that appear to be the somatic mesoderm (M). Embryo e, after germ-band retraction. Expression persists in the developing somatic musculature (SM) and in the AMG and PMG as they fuse to form the midgut (MG). (B) Cytogenetic localization of the dmyc1 locus. A dmyc1 cDNA probe identifies a unique hybridization signal at 3D4–7 on Drosophila polytene chromosomes (arrowhead). Polytene segments 3 c, d, and e are indicated. (C) Confirmation of chromosomal localization by detection of dmyc1 in YACs bearing various segments of the Drosophila X chromosome. Primers directed to sequences that amplify the bHLH/LZ region of dmyc1 were used in a PCR screen of a series of 3CD-containing YACs. The 300-bp PCR amplification product was detected only in YAC 6 (containing regions 3D1–2 to 3E2–3) and YAC 8 (containing regions 3D4–3D7), and in the dmyc1 cDNA positive control.