Abstract
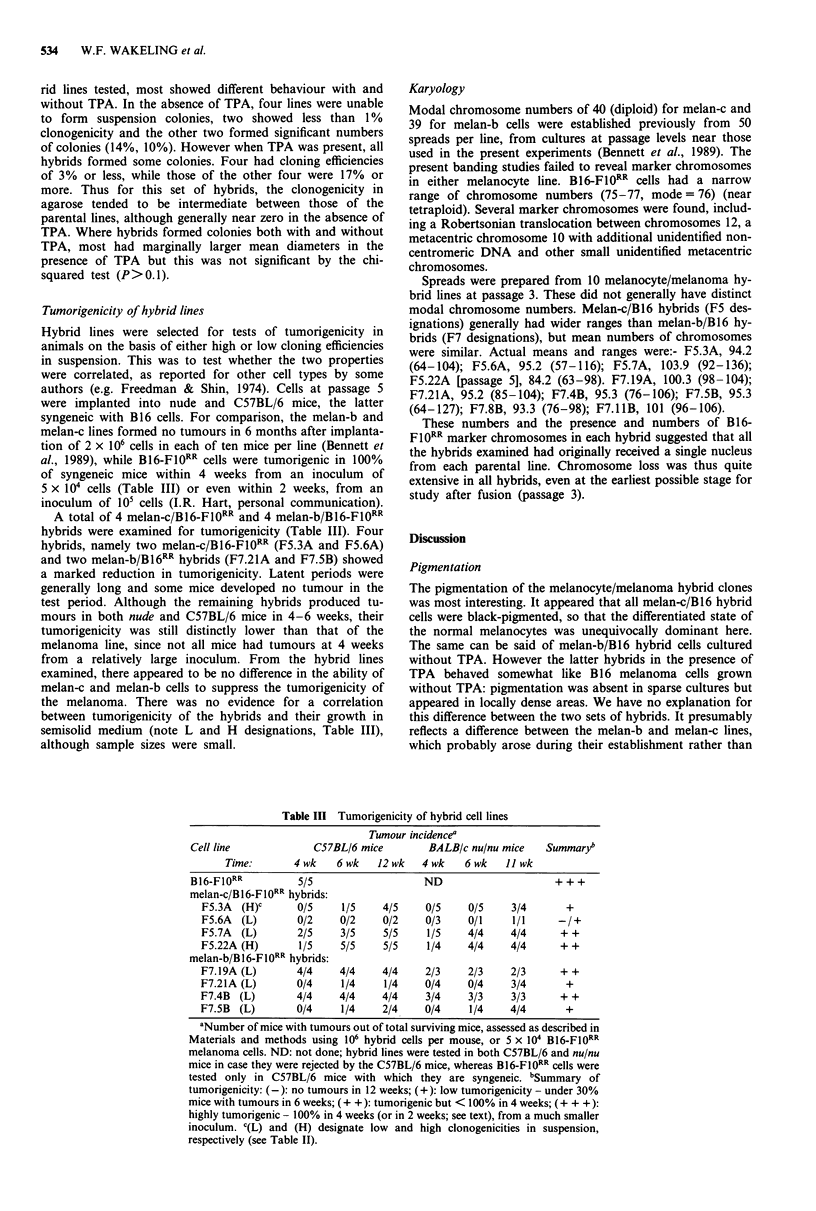
Murine and human melanoma cells differ relatively reliably from non-tumorigenic melanocytes in certain biological properties. When cultured at low pH, melanocytes tend to be pigmented and melanoma cells unpigmented. The growth of virtually all metastatic melanoma cells is inhibited by phorbol esters such as TPA (12-O-tetradecanoyl phorbol-13-acetate), which stimulate melanocyte growth. Melanocytes fail to grow in suspension culture or produce tumours when implanted in animals, while many melanoma lines can do both. Here we studied which of these properties were dominant in hybrid cells formed by fusion of drug-resistant murine B16-F10RR melanoma cells to melanocytes of the albino and brown lines, melan-c and melan-b. The albino melanocytes are unpigmented but well-differentiated, the brown melanocytes produce pale brown pigment and the melanoma cells are unpigmented under the conditions used. All hybrid colonies observed produced black pigment, except some melan-b/melanoma hybrids when growing sparsely with TPA. Thus pigmentation was generally dominant. 14/15 hybrid lines showed stimulation of proliferation by TPA, as do melanocytes. Most hybrid lines showed no or reduced capacity for growth in suspension, though some grew better in suspension when TPA was present. There was marked suppression of the tumorigenicity of the parental melanoma cells in 4/8 hybrids examined, and tumorigenicity was reduced in the others, despite considerable chromosome loss by the passage level tested. Thus most properties of the non-tumorigenic pigment cells were dominant, as often observed for other cell lineages, and providing further evidence for gene loss in the genesis of malignant melanoma.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albino A. P., Houghton A. N., Eisinger M., Lee J. S., Kantor R. R., Oliff A. I., Old L. J. Class II histocompatibility antigen expression in human melanocytes transformed by Harvey murine sarcoma virus (Ha-MSV) and Kirsten MSV retroviruses. J Exp Med. 1986 Nov 1;164(5):1710–1722. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.5.1710. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bale S. J., Dracopoli N. C., Tucker M. A., Clark W. H., Jr, Fraser M. C., Stanger B. Z., Green P., Donis-Keller H., Housman D. E., Greene M. H. Mapping the gene for hereditary cutaneous malignant melanoma-dysplastic nevus to chromosome 1p. N Engl J Med. 1989 May 25;320(21):1367–1372. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198905253202102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett D. C., Cooper P. J., Dexter T. J., Devlin L. M., Heasman J., Nester B. Cloned mouse melanocyte lines carrying the germline mutations albino and brown: complementation in culture. Development. 1989 Feb;105(2):379–385. doi: 10.1242/dev.105.2.379. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett D. C., Cooper P. J., Hart I. R. A line of non-tumorigenic mouse melanocytes, syngeneic with the B16 melanoma and requiring a tumour promoter for growth. Int J Cancer. 1987 Mar 15;39(3):414–418. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910390324. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bennett D. C., Dexter T. J., Ormerod E. J., Hart I. R. Increased experimental metastatic capacity of a murine melanoma following induction of differentiation. Cancer Res. 1986 Jul;46(7):3239–3244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blochlinger K., Diggelmann H. Hygromycin B phosphotransferase as a selectable marker for DNA transfer experiments with higher eucaryotic cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;4(12):2929–2931. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.12.2929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceci J. D., Siracusa L. D., Jenkins N. A., Copeland N. G. A molecular genetic linkage map of mouse chromosome 4 including the localization of several proto-oncogenes. Genomics. 1989 Nov;5(4):699–709. doi: 10.1016/0888-7543(89)90111-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cook P. J., Doll R., Fellingham S. A. A mathematical model for the age distribution of cancer in man. Int J Cancer. 1969 Jan 15;4(1):93–112. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910040113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A. Oncogenes and anti-oncogenes. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 1990 Apr;2(2):285–295. doi: 10.1016/0955-0674(90)90021-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowell J. K., Franks L. M. The ability of normal mouse cells to reduce the malignant potential of transformed mouse bladder epithelial cells depends on their somatic origin. Int J Cancer. 1984 May 15;33(5):657–667. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910330517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dotto G. P., Moellmann G., Ghosh S., Edwards M., Halaban R. Transformation of murine melanocytes by basic fibroblast growth factor cDNA and oncogenes and selective suppression of the transformed phenotype in a reconstituted cutaneous environment. J Cell Biol. 1989 Dec;109(6 Pt 1):3115–3128. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.6.3115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisinger M., Marko O. Selective proliferation of normal human melanocytes in vitro in the presence of phorbol ester and cholera toxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):2018–2022. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.2018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans E. P., Burtenshaw M. D., Brown B. B., Hennion R., Harris H. The analysis of malignancy by cell fusion. IX. Re-examination and clarification of the cytogenetic problem. J Cell Sci. 1982 Aug;56:113–130. doi: 10.1242/jcs.56.1.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler I. J. Biological behavior of malignant melanoma cells correlated to their survival in vivo. Cancer Res. 1975 Jan;35(1):218–224. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fougère C., Ruiz F., Ephrussi B. Gene dosage dependence of pigment synthesis in melanoma x fibroblast hybrids (hamster cells-mouse fibroblast-DOPA-oxidase-irradiation). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):330–334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman V. H., Shin S. I. Cellular tumorigenicity in nude mice: correlation with cell growth in semi-solid medium. Cell. 1974 Dec;3(4):355–359. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(74)90050-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Halaban R., Nordlund J., Francke U., Moellmann G., Eisenstadt J. M. Supermelanotic hybrids derived from mouse melanomas and normal mouse cells. Somatic Cell Genet. 1980 Jan;6(1):29–44. doi: 10.1007/BF01538694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris H., Miller O. J., Klein G., Worst P., Tachibana T. Suppression of malignancy by cell fusion. Nature. 1969 Jul 26;223(5204):363–368. doi: 10.1038/223363a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris H. The role of differentiation in the suppression of malignancy. J Cell Sci. 1990 Sep;97(Pt 1):5–10. doi: 10.1242/jcs.97.1.5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herlyn M., Kath R., Williams N., Valyi-Nagy I., Rodeck U. Growth-regulatory factors for normal, premalignant, and malignant human cells in vitro. Adv Cancer Res. 1990;54:213–234. doi: 10.1016/s0065-230x(08)60812-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghton A. N., Real F. X., Davis L. J., Cordon-Cardo C., Old L. J. Phenotypic heterogeneity of melanoma. Relation to the differentiation program of melanoma cells. J Exp Med. 1987 Mar 1;165(3):812–829. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.3.812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang H. J., Yee J. K., Shew J. Y., Chen P. L., Bookstein R., Friedmann T., Lee E. Y., Lee W. H. Suppression of the neoplastic phenotype by replacement of the RB gene in human cancer cells. Science. 1988 Dec 16;242(4885):1563–1566. doi: 10.1126/science.3201247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonasson J., Povey S., Harris H. The analysis of malignancy by cell fusion. VII. Cytogenetic analysis of hybrids between malignant and diploid cells and of tumours derived from them. J Cell Sci. 1977 Apr;24:217–254. doi: 10.1242/jcs.24.1.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLEFIELD J. W. SELECTION OF HYBRIDS FROM MATINGS OF FIBROBLASTS IN VITRO AND THEIR PRESUMED RECOMBINANTS. Science. 1964 Aug 14;145(3633):709–710. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3633.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laskin J. D., Mufson R. A., Weinstein I. B., Engelhardt D. L. Identification of a distinct phase during melanogenesis that is sensitive to extracellular pH and ionic strength. J Cell Physiol. 1980 Jun;103(3):467–474. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041030312. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muschel R. J., Nakahara K., Chu E., Pozzatti R., Liotta L. A. Karyotypic analysis of diploid or near diploid metastatic Harvey ras transformed rat embryo fibroblasts. Cancer Res. 1986 Aug;46(8):4104–4108. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nigro J. M., Baker S. J., Preisinger A. C., Jessup J. M., Hostetter R., Cleary K., Bigner S. H., Davidson N., Baylin S., Devilee P. Mutations in the p53 gene occur in diverse human tumour types. Nature. 1989 Dec 7;342(6250):705–708. doi: 10.1038/342705a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pereira-Smith O. M., Smith J. R. Genetic analysis of indefinite division in human cells: identification of four complementation groups. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Aug;85(16):6042–6046. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.16.6042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato C., Ito S., Takeuchi T. Establishment of a mouse melanocyte clone which synthesizes both eumelanin and pheomelanin. Cell Struct Funct. 1985 Dec;10(4):421–425. doi: 10.1247/csf.10.421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanbridge E. J., Ceredig R. Growth-regulatory control of human cell hybrids in nude mice. Cancer Res. 1981 Feb;41(2):573–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanbridge E. J., Der C. J., Doersen C. J., Nishimi R. Y., Peehl D. M., Weissman B. E., Wilkinson J. E. Human cell hybrids: analysis of transformation and tumorigenicity. Science. 1982 Jan 15;215(4530):252–259. doi: 10.1126/science.7053574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoler A., Bouck N. Identification of a single chromosome in the normal human genome essential for suppression of hamster cell transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):570–574. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura A., Halaban R., Moellmann G., Cowan J. M., Lerner M. R., Lerner A. B. Normal murine melanocytes in culture. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol. 1987 Jul;23(7):519–522. doi: 10.1007/BF02628423. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trent J. M., Leong S. P., Meyskens F. L. Chromosome alterations in human malignant melanoma. Carcinog Compr Surv. 1989;11:165–186. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trent J. M., Stanbridge E. J., McBride H. L., Meese E. U., Casey G., Araujo D. E., Witkowski C. M., Nagle R. B. Tumorigenicity in human melanoma cell lines controlled by introduction of human chromosome 6. Science. 1990 Feb 2;247(4942):568–571. doi: 10.1126/science.2300817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener F., Cochran A., Klein G., Harris H. Genetic determinants of morphological differentiation in hybrid tumors. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1972 Feb;48(2):465–486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiener F., Klein G., Harris H. The analysis of malignancy by cell fusion. IV. Hybrid between tumour cells and a malignant L cell derivative. J Cell Sci. 1973 Jan;12(1):253–261. doi: 10.1242/jcs.12.1.253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]