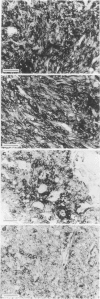
Abstract
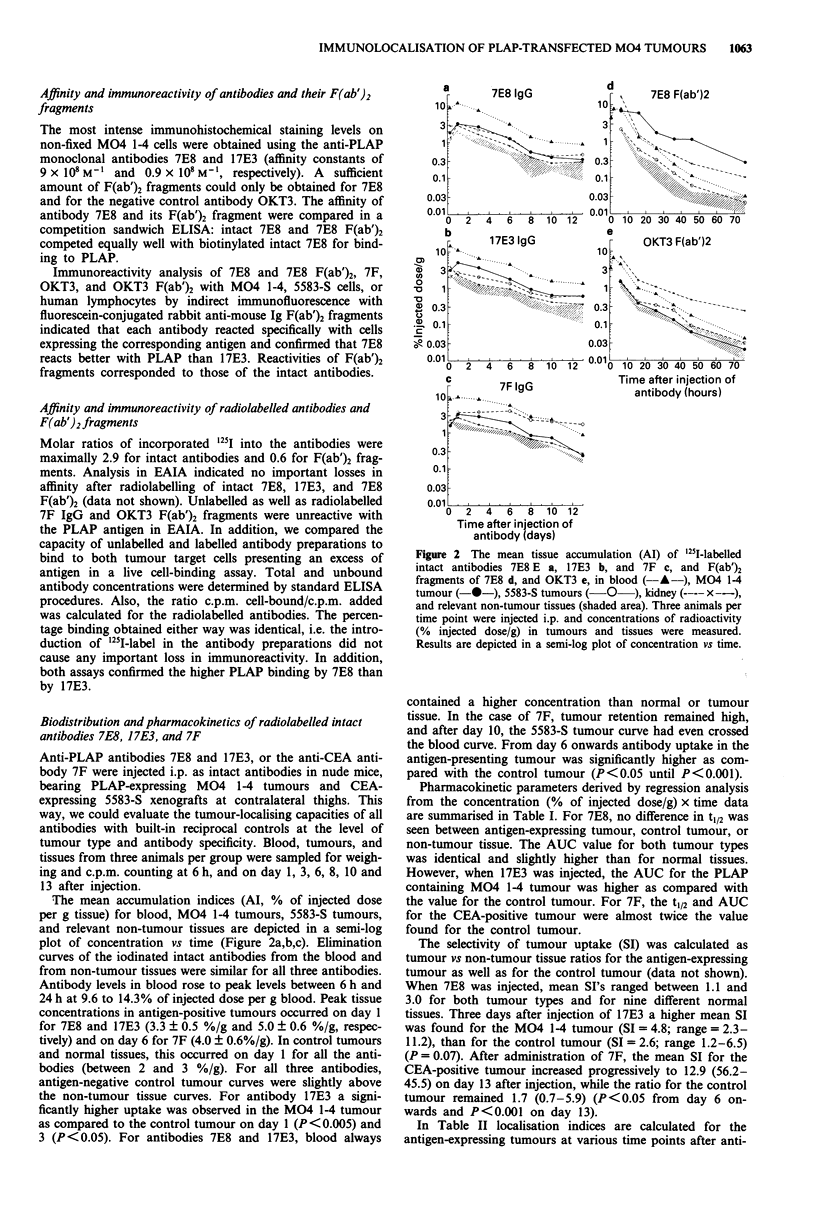
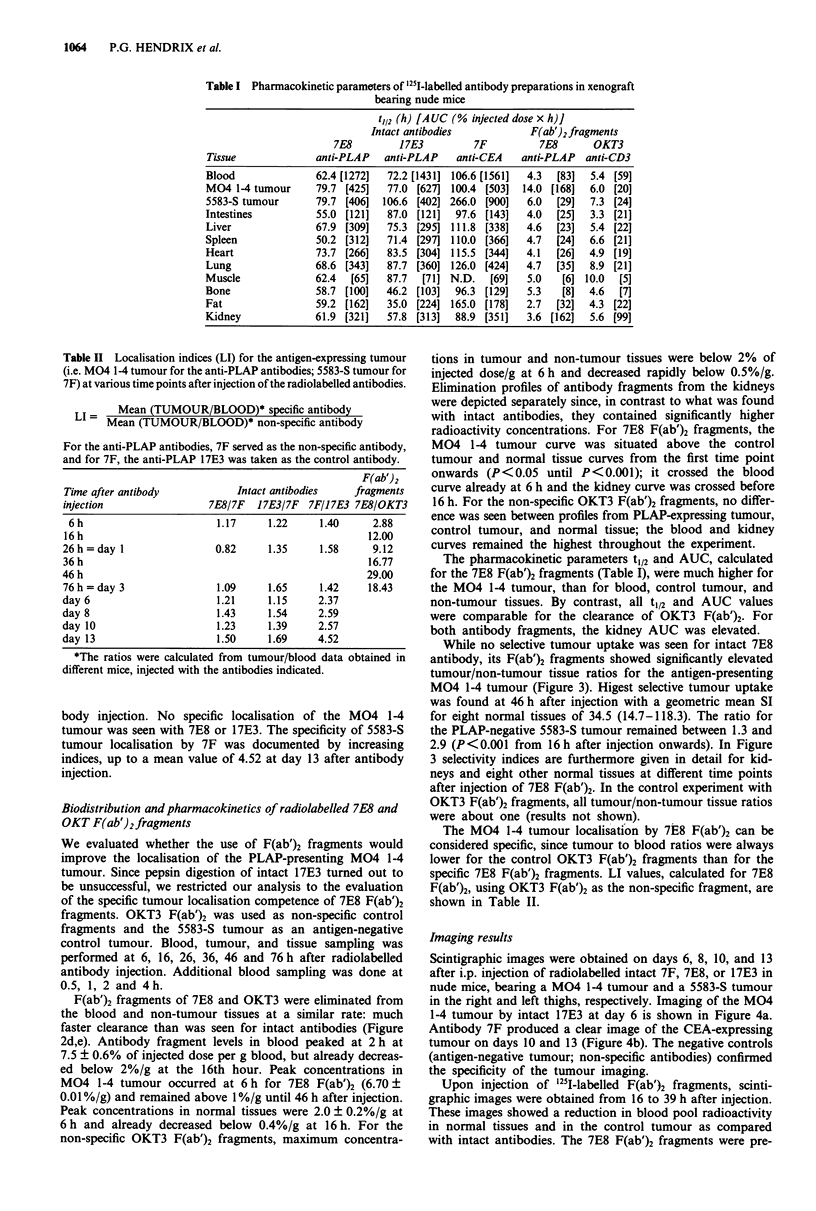
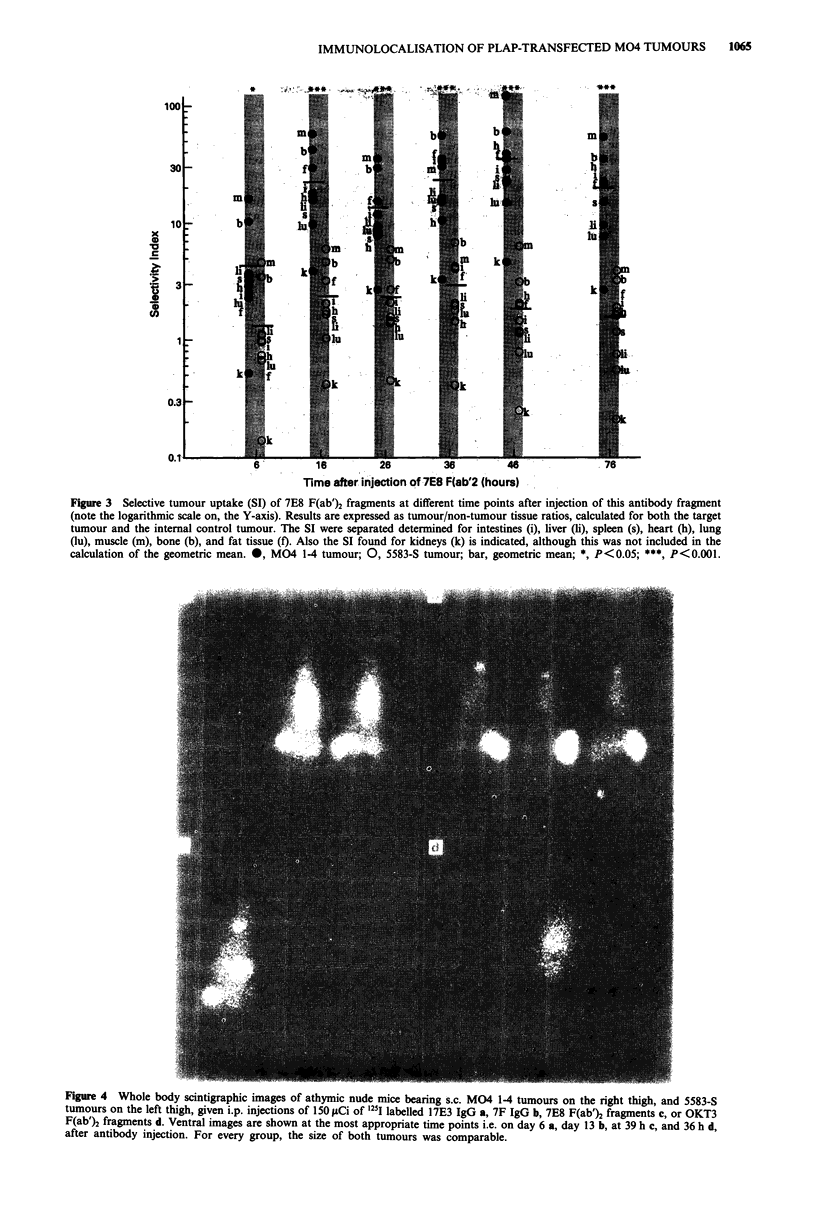
Immunotargeting of PLAP-expressing tumours was studied for two radioiodinated, highly specific anti-PLAP monoclonal antibodies, 7E8 and 17E3, differing 10-fold in affinity, as well as for 7E8 F(ab')2 fragments. An anti-CEA monoclonal antibody or anti-CD3 F(ab')2 fragments were used as controls. Specific and non-specific targeting was examined in nude mice simultaneously grafted with PLAP-positive tumours derived from MO4 1-4 cells, and CEA-positive tumours, derived from 5583-S cells. Results indicated that (1) MO4 1-4 tumours, with a stable expression of PLAP on the plasma membrane, represent a useful new in vivo model for immunodirected tumour targeting; (2) differences in antibody affinity for PLAP in vitro are not reflected in antibody avidity for tumour cells in vivo; and (3) excellent selective and specific localisation of the PLAP-positive tumours is achieved when 7E8 F(ab')2 fragments are used. The high tumour/blood ratios (10.7 +/- 3.9 at 46 h after injection) were due to a much faster blood clearance of 7E8 F(ab')2 fragments. At this time point, the mean tumour/non-tumour tissue ratio was as high as 34.5, and the mean specific localisation index was 29.0. As expected, the F(ab')2 fragments provided high tumour imaging efficiency on gamma camera recording. These data imply important potentials of the PLAP/anti-PLAP system for immunolocalisation and therapy in patients, but also emphasise that in vitro criteria alone are not reflected in in vivo tumour localisation capacities of antibodies.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bale W. F., Contreras M. A., Grady E. D. Factors influencing localization of labeled antibodies in tumors. Cancer Res. 1980 Aug;40(8 Pt 2):2965–2972. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Billiau A., Sobis H., Eyssen H., Van den Berghe H. Non-infectious intracisternal A-type particles in a sarcoma-positive, leukemia-negative mouse cell line transformed by murine sarcoma virus (MSV). Arch Gesamte Virusforsch. 1973;43(4):345–351. doi: 10.1007/BF01556151. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal R. D., Sharkey R. M., Kashi R., Goldenberg D. M. Comparison of therapeutic efficacy and host toxicity of two different 131I-labelled antibodies and their fragments in the GW-39 colonic cancer xenograft model. Int J Cancer. 1989 Aug 15;44(2):292–300. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910440218. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchegger F., Haskell C. M., Schreyer M., Scazziga B. R., Randin S., Carrel S., Mach J. P. Radiolabeled fragments of monoclonal antibodies against carcinoembryonic antigen for localization of human colon carcinoma grafted into nude mice. J Exp Med. 1983 Aug 1;158(2):413–427. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.2.413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchegger F., Mach J. P., Leonnard P., Carrel S. Selective tumor localization of radiolabeled anti-human melanoma monoclonal antibody fragment demonstrated in the nude mouse model. Cancer. 1986 Aug 1;58(3):655–662. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19860801)58:3<655::aid-cncr2820580310>3.0.co;2-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchsbaum D. J., Sinkule J. A., Stites M. S., Fodor P. A., Hanna D. E., Ford S. M., Warber-Matich S. L., Juni J. E., Foon K. A. Localization and imaging with radioiodine-labeled monoclonal antibodies in a xenogeneic tumor model for human B-cell lymphoma. Cancer Res. 1988 May 1;48(9):2475–2482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang C. H., Angellis D., Fishman W. H. Presence of the rare D-variant heat-stable, placental-type alkaline phosphatase in normal human testis. Cancer Res. 1980 May;40(5):1506–1510. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covell D. G., Barbet J., Holton O. D., Black C. D., Parker R. J., Weinstein J. N. Pharmacokinetics of monoclonal immunoglobulin G1, F(ab')2, and Fab' in mice. Cancer Res. 1986 Aug;46(8):3969–3978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Broe M. E., Pollet D. E. Multicenter evaluation of human placental alkaline phosphatase as a possible tumor-associated antigen in serum. Clin Chem. 1988 Oct;34(10):1995–1999. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eccles S. A., Purvies H. P., Styles J. M., Hobbs S. M., Dean C. J. Pharmacokinetic studies of radiolabelled rat monoclonal antibodies recognising syngeneic sarcoma antigens. I. Comparison of IgG subclasses. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1989;30(1):5–12. doi: 10.1007/BF01665024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endo K., Kamma H., Ogata T. Radiolocalization of xenografted human lung cancer with monoclonal antibody 8 in nude mice. Cancer Res. 1987 Oct 15;47(20):5427–5432. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GREENWOOD F. C., HUNTER W. M., GLOVER J. S. THE PREPARATION OF I-131-LABELLED HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE OF HIGH SPECIFIC RADIOACTIVITY. Biochem J. 1963 Oct;89:114–123. doi: 10.1042/bj0890114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldstein D. J., Rogers C., Harris H. A search for trace expression of placental-like alkaline phosphatase in non-malignant human tissues: demonstration of its occurrence in lung, cervix, testis and thymus. Clin Chim Acta. 1982 Oct 13;125(1):63–75. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(82)90046-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gossrau R. Azoindoxylverfahren zum Hydrolasennachweis. IV. Zur Eignung verschiedener Diazoniumsalze. Histochemistry. 1978 Sep 28;57(4):323–342. doi: 10.1007/BF00492668. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedin A., Wahren B., Hammarström S. Tumor localization of CEA-containing human tumors in nude mice by means of monoclonal anti-CEA antibodies. Int J Cancer. 1982 Nov 15;30(5):547–552. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910300503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrix P. G., Hoylaerts M. F., Nouwen E. J., De Broe M. E. Enzyme immunoassay of human placental and germ-cell alkaline phosphatase in serum. Clin Chem. 1990 Oct;36(10):1793–1799. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herlyn D., Powe J., Alavi A., Mattis J. A., Herlyn M., Ernst C., Vaum R., Koprowski H. Radioimmunodetection of human tumor xenografts by monoclonal antibodies. Cancer Res. 1983 Jun;43(6):2731–2735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeppsson A., Wahren B., Millán J. L., Stigbrand T. Tumour and cellular localization by use of monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies to placental alkaline phosphatase. Br J Cancer. 1984 Feb;49(2):123–128. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1984.23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshida K., Wahren B. Placental-like alkaline phosphatase in seminoma. Urol Res. 1990;18(2):87–92. doi: 10.1007/BF00302465. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamoyi E., Nisonoff A. Preparation of F(ab')2 fragments from mouse IgG of various subclasses. J Immunol Methods. 1983 Jan 28;56(2):235–243. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(83)90415-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mann B. D., Cohen M. B., Saxton R. E., Morton D. L., Benedict W. F., Korn E. L., Spolter L., Graham L. S., Chang C. C., Burk M. W. Imaging of human tumor xenografts in nude mice with radiolabeled monoclonal antibodies. Limitations of specificity due to nonspecific uptake of antibody. Cancer. 1984 Oct 1;54(7):1318–1327. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19841001)54:7<1318::aid-cncr2820540715>3.0.co;2-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mareel M., De Ridder L., De Brabander M., Vakaet L. Characterization of spontaneous, chemicak, and viral transformants of a C3H/3T3-type mouse cell line by transplantation into young chick blastoderms. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1975 Apr;54(4):923–929. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mather S. J., Durbin H., Taylor-Papadimitriou J. Identification of immunoreactive monoclonal antibody fragments for improved immunoscintigraphy. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Feb 11;96(2):255–264. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90322-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matzku S., Kirchgessner H., Dippold W. G., Brüggen J. Immunoreactivity of monoclonal anti-melanoma antibodies in relation to the amount of radioactive iodine substituted to the antibody molecule. Eur J Nucl Med. 1985;11(6-7):260–264. doi: 10.1007/BF00279081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meyvisch C., Mareel M. Influence of implantation site of MO4 cell aggregates on the formation of metastases. Invasion Metastasis. 1982;2(1):51–60. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millán J. L. Molecular cloning and sequence analysis of human placental alkaline phosphatase. J Biol Chem. 1986 Mar 5;261(7):3112–3115. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Millán J. L., Stigbrand T. Antigenic determinants of human placental and testicular placental-like alkaline phosphatases as mapped by monoclonal antibodies. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Oct 17;136(1):1–7. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07697.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moshakis V., McIlhinney R., Raghavan D., Neville A. M. Monoclonal antibodies to detect human tumours: an experimental approach. J Clin Pathol. 1981 Mar;34(3):314–319. doi: 10.1136/jcp.34.3.314. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nouwen E. J., Hendrix P. G., Dauwe S., Eerdekens M. W., De Broe M. E. Tumor markers in the human ovary and its neoplasms. A comparative immunohistochemical study. Am J Pathol. 1987 Feb;126(2):230–242. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nouwen E. J., Pollet D. E., Eerdekens M. W., Hendrix P. G., Briers T. W., De Broe M. E. Immunohistochemical localization of placental alkaline phosphatase, carcinoembryonic antigen, and cancer antigen 125 in normal and neoplastic human lung. Cancer Res. 1986 Feb;46(2):866–876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pimm M. V., Andrew S. M., Baldwin R. W. Blood and tissue kinetics of radiolabelled anti-CEA monoclonal antibody and F(ab)2 and Fab fragments in nude mice with human tumour xenografts: implications for tumour imaging and radioimmunotherapy. Nucl Med Commun. 1989 Aug;10(8):585–593. doi: 10.1097/00006231-198908010-00007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pimm M. V., Baldwin R. W. Comparative biodistributions and rates of catabolism of radiolabelled anti-CEA monoclonal antibody and control immunoglobulin in nude mice with human tumour xenografts showing specific antibody localization. Eur J Nucl Med. 1987;13(5):258–263. doi: 10.1007/BF00252604. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pimm M. V., Baldwin R. W. Comparative tumour localization properties of radiolabelled monoclonal antibody preparations of defined immunoreactivities. Eur J Nucl Med. 1987;13(7):348–352. doi: 10.1007/BF00252993. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pimm M. V., Perkins A. C., Baldwin R. W. Diverse characteristics of 111In labelled anti-CEA monoclonal antibodies for tumour immunoscintigraphy: radiolabelling, biodistribution and imaging studies in mice with human tumour xenografts. Eur J Nucl Med. 1987;12(10):515–521. doi: 10.1007/BF00620477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robson E. B., Harris H. Genetics of the alkaline phosphatase polymorphism of the human placenta. Nature. 1965 Sep 18;207(5003):1257–1259. doi: 10.1038/2071257a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakahara H., Endo K., Koizumi M., Nakashima T., Kunimatsu M., Watanabe Y., Kawamura Y., Nakamura T., Tanaka H., Kotoura Y. Relationship between in vitro binding activity and in vivo tumor accumulation of radiolabeled monoclonal antibodies. J Nucl Med. 1988 Feb;29(2):235–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharkey R. M., Gold D. V., Aninipot R., Vagg R., Ballance C., Newman E. S., Ostella F., Hansen H. J., Goldenberg D. M. Comparison of tumor targeting in nude mice by murine monoclonal antibodies directed against different human colorectal cancer antigens. Cancer Res. 1990 Feb 1;50(3 Suppl):828s–834s. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stigbrand T., Hietala S. O., Johansson B., Makiya R., Riklund K., Ekelund L. Tumour radioimmunolocalization in nude mice by use of antiplacental alkaline phosphatase monoclonal antibodies. Tumour Biol. 1989;10(5):243–251. doi: 10.1159/000217621. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verstijnen C. P., Arends J. W., Moerkerk P. T., Geraedts J. P., Sekikawa K., Uitendaal M. P., Bosman F. T. The establishment and characterization of two new cell lines derived from a single human colonic adenocarcinoma. Virchows Arch B Cell Pathol Incl Mol Pathol. 1987;53(4):191–197. doi: 10.1007/BF02890243. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wahl R. L., Parker C. W., Philpott G. W. Improved radioimaging and tumor localization with monoclonal F(ab')2. J Nucl Med. 1983 Apr;24(4):316–325. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]