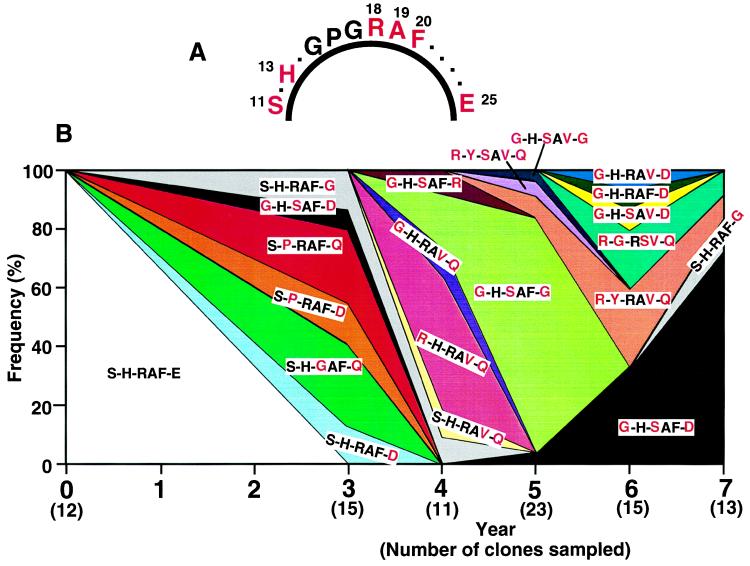
Figure 4.
Population dynamics of HIV variants within patient A. (A) The amino acid stretch including the crown of the V3 loop. The amino acid sites shown by single letters in red, where higher numbers of amino acid substitutions were observed, are thought to be responsible for antigenic variation in HIV. (B) Frequency change of HIV variants within patient A. We classified the HIV variants according to amino acid variation at the red sites in A.