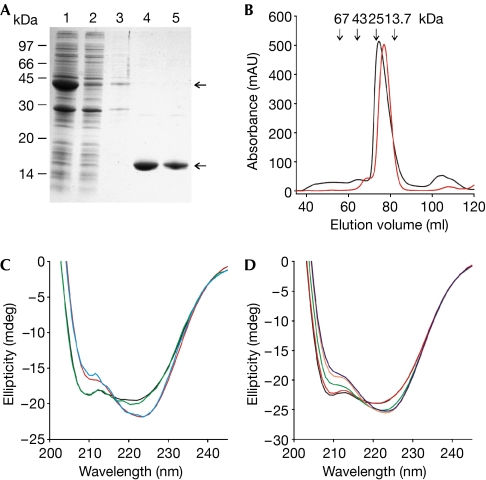
Figure 1.
Purification and characterization of the CNBD protein. (A) The CNBD–GST fusion protein was expressed in Escherichia coli and affinity purified (lane 1: column input; lane 2: non-bound; lane 3: wash; lanes 4 and 5: elution of the CNBD protein after thrombin cleavage). Upper and lower arrows indicate the CNBD–GST fusion protein and the cleaved CNBD protein, respectively. Coomassie blue staining of an SDS–polyacrylamide gel. (B) Gel-filtration profile of the purified CNBD protein. Red trace: elution profile of the native CNBD protein; black trace: profile of the CNBD protein after denaturation and refolding. Arrows indicate the elution volume of marker proteins. (C) CD spectra of the purified CNBD protein (8.2 μM) before unfolding (blue), after refolding in the absence of cAMP (black), after refolding in the presence of cAMP (15 μM, red) and of the R348A mutant in the absence of cAMP (green). (D) CD spectra of the refolded CNBD protein (11.4 μM) titrated with cAMP at different concentrations (black, 0 μM; red, 5 μM; green, 10 μM; orange, 15 μM; blue, 20 μM). CD, circular dichroism; CNBD, cyclic nucleotide-binding domain; GST, glutathione-S-transferase.