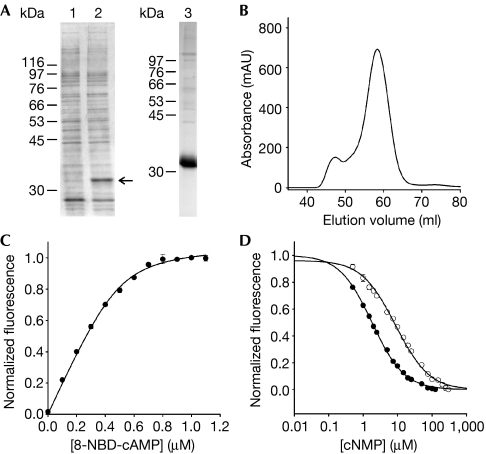
Figure 4.
Ligand binding of the full-length mlCNG protein. (A) mlCNG detected by Coomassie blue staining (arrow) in bacterial lysates (lane 1: no induction; lane 2: IPTG induction). mlCNG protein purified by Co2+-affinity chromatography (lane 3). (B) Size-exclusion chromatography of the purified mlCNG protein. Most of the mlCNG protein eluted at 58.3 ml. (C) Normalized increase of fluorescence of 8-NBD-cAMP on binding to mlCNG protein (5 μM). 8-NBD-cAMP fluorescence in the absence of the mlCNG protein was subtracted. The solid line represents a non-linear least-squares fit to Δ F=RL · x (equation (3), see supplementary information online). The KD value was 17.3 nM. (D) Competition between 8-NBD-cAMP (0.5 μM) and cAMP (closed circles) or cGMP (open circles) for binding to the mlCNG protein (0.3 μM). The solid lines represent a nonlinear least-squares fit to Δ F=RL · x (equation (7), see supplementary information online). The KD values were 71.3 nM (cAMP) and 363.9 nM (cGMP). IPTG, isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactopyranoside; mlCNG, Mesorhizobium loti cyclic nucleotide-gated channel; 8-NBD-cAMP, 8-[[2-[(7-Nitro-4-benzofurazanyl)amino]ethyl]thio]adenosine–3′,5′-cyclic monophosphate.