Figure 1. NFAT induces a specific program of gene expression in anergic T cells.
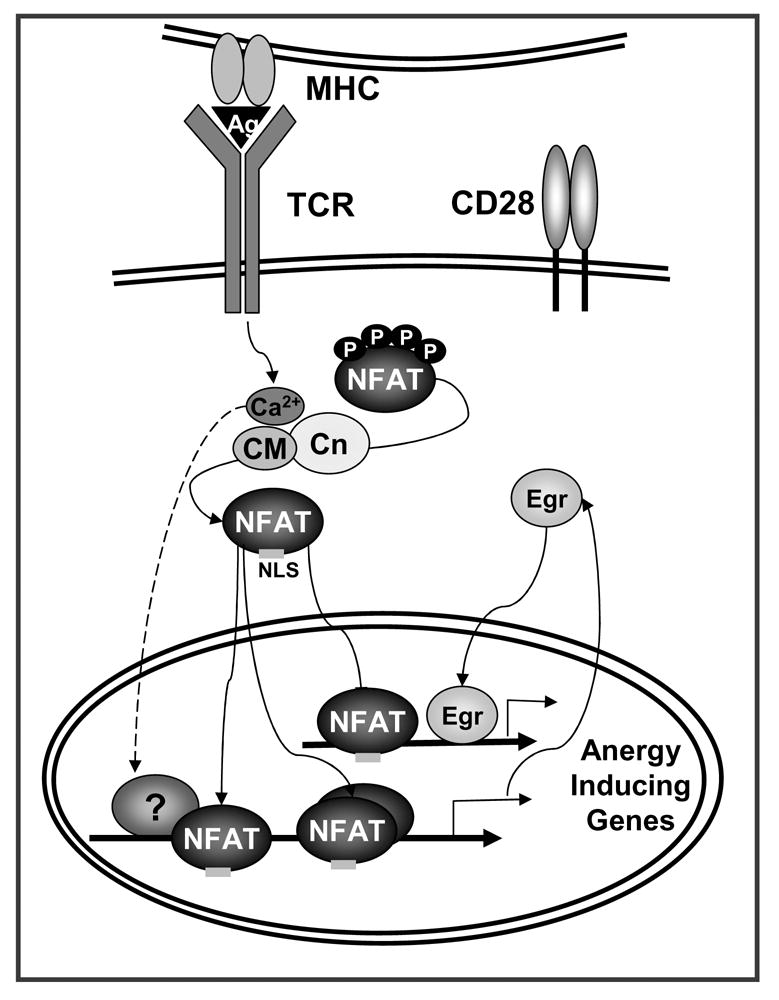
TCR engagement without concomitant costimulation results in the unbalance activation of calcium signaling in the absence of full activation of other pathways (i.e. Ras/MAPK, PKC, IKK). Sustained increased intracellular calcium activates the calmodulin (CM) dependent phosphatase calcineurin (Cn) which dephosphorylates NFAT, exposing a nuclear localization signal (NLS) and inducing NFAT nuclear translocation. In the absence of AP-1 proteins, NFAT induces an anergy-inducing program of gene expression. NFAT also upregulates the expression of Egr2 and Egr3 (Egr) that contribute in cooperation with NFAT or in an independent manner, to activate the expression of anergy-inducing genes. The proteins encoded by those genes (e.g. Itch, Grail, Cbl-b, DGKα, Ikaros) will cause dampening of TCR signaling and IL-2 silencing in anergic T cells.
