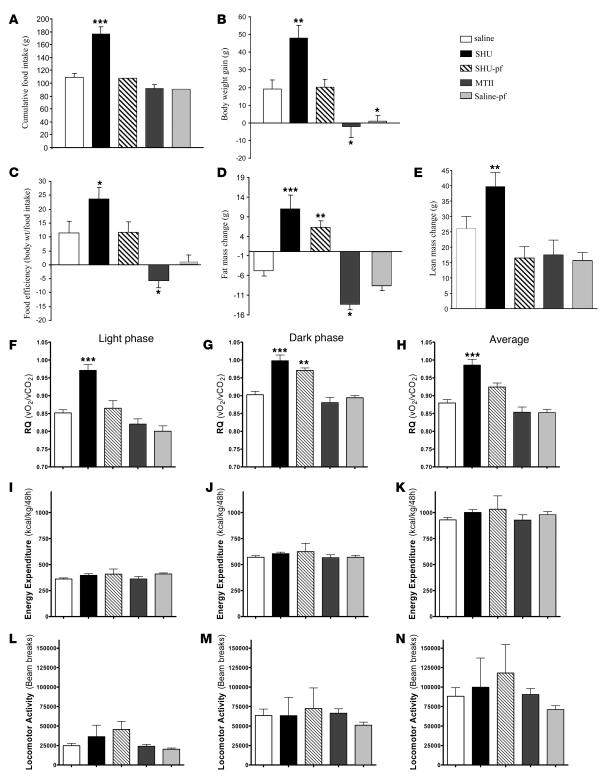
Figure 1. Effect of a 7-day i.c.v. SHU9119 (24 nmol/d) and MTII (1 nmol/d) infusion on cumulative food intake (A), body weight gain (B), food efficiency (C), fat mass change (D), lean mass change (E), RQ (F–H), energy expenditure (I–K), and locomotor activity (L–N).
Food efficiency was calculated as the ratio between body weight gain over the 7-day experimental period and cumulative food intake and was expressed as a percentage. Body fat was determined by NMR imaging. RQ, energy expenditure, and locomotor activity were measured over the last 3 days of the experiment during the light and dark phases. Values are mean ± SEM of 7–8 animals per group. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001 versus controls.