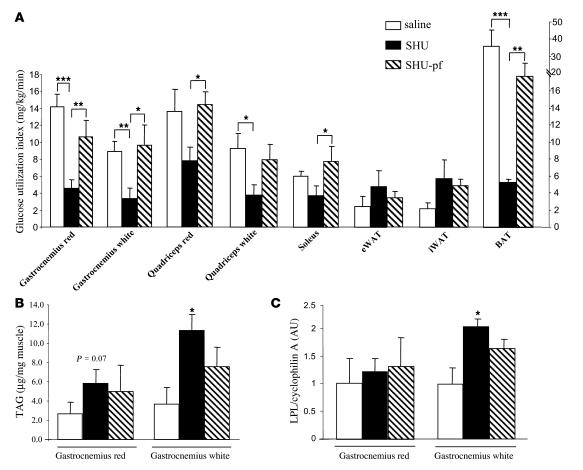
Figure 6. Effect of a 7-day i.c.v. SHU9119 infusion (24 nmol/d) in the regulation of insulin action on peripheral glucose uptake and production.
(A) Insulin-stimulated glucose utilization measured during euglycemic-hyperinsulinemic clamps in several types of muscle: gastrocnemius red, gastrocnemius white, quadriceps red, quadriceps white, soleus, epididymal WAT, inguinal WAT (iWAT), and BAT. (B) TAG content in gastrocnemius red and gastrocnemius white. (C) LPL mRNA expression in gastrocnemius red and gastrocnemius white. During euglycemic-hyperinsulinemic clamps, the rates of glucose infusion and hepatic glucose production were unchanged in SHU9119- compared with vehicle-treated rats. Glucose infusion rates (in mg/kg/min): vehicle 19.6 ± 1.1; SHU9119-ad lib 18.4 ± 1.2; SHU9119-pf 18.5 ± 0.6. Hepatic glucose production (in mg/kg/min): vehicle –0.8 ± 1.7; SHU9119-ad lib –3.3 ± 2.2; SHU9119-pf –1.9 ± 1. Values are mean ± SEM of 6–7 animals per group. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001.