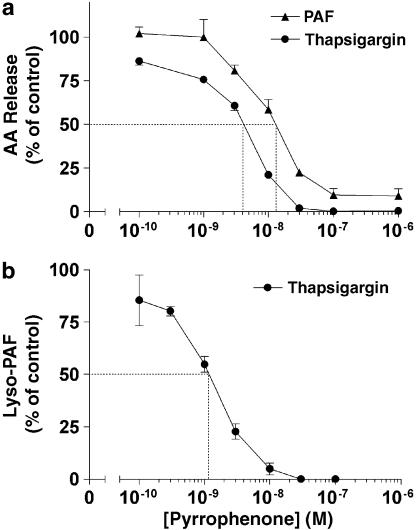
Figure 3.
Inhibitory effects of pyrrophenone on AA and lyso-PAF release in activated human PMN. (a) PMN suspensions (37°C, 5 × 106 cells ml−1) were incubated in the presence of increasing concentrations of pyrrophenone, then stimulated with either 100 nM thapsigargin or 300 nM PAF for 5 and 2 min, respectively, as described in Methods. Incubations were stopped by the addition of 0.5 volume of a cold (4°C) stop solution (MeOH/MeCN, 1/1, v/v) containing 12.5 ng of both 19-OH-PGB2 and PGB2, and 20 ng of 2H8-AA as internal standards. Supernatants were collected and analyzed for AA content by LC/MS as described in Methods. (b) PMN suspensions (37°C, 5 × 106 cells ml−1) were stimulated with 100 nM thapsigargin for 10 min as described in Methods. Incubations were stopped by the addition of 1 volume of EtOH containing 5 ng of 2H4-PAF. Supernatants were collected and lyso-PAF was extracted and analyzed as described in Methods. In all experimental settings, 0.3 U ml−1 ADA and pyrrophenone were added 10 min before the addition of the stimuli. Data represent the mean (±s.e.m.) of three separate experiments, each performed in duplicate.