Figure 3.
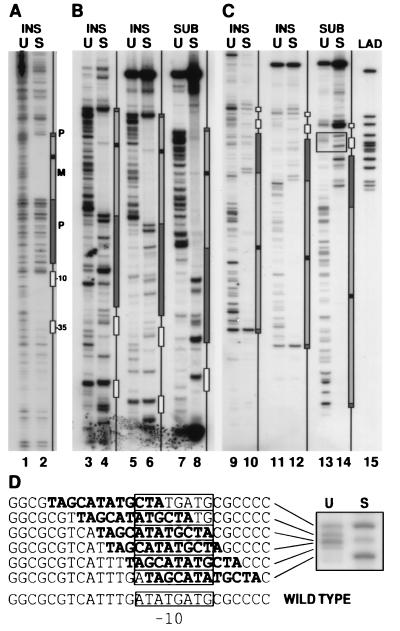
Genetic footprinting of supF. (A) Analysis of 36-bp insertional mutations in the plasmid πAN13. DNA from the unselected (U) and selected (S) libraries of mutant supF was used as template for a PCR containing a primer complementary to the insert oligonucleotide, paired with a radiolabeled primer complementary to a region 160 bp upstream of the transcription start site (π267L). A schematic diagram of the supF gene is shown to the right, aligned with the corresponding PCR products. Sequenced plasmid DNA and PCR products from selected sequenced mutations were run adjacent to the footprinted DNA as molecular weight markers and were used to draw the boxes representing various regions of the supF gene (boxes marked −10 and −35 correspond to promoter elements; P, regions of precursor tRNA that are removed upon processing; M, mature tRNA. Black box within the mature tRNA corresponds to the variable loop). (B and C) Analysis of libraries of 36-bp insertional (INS) or 12-bp substitution (SUB) mutations in the plasmid πchloro. In B, the labeled primer (CAM60supF) was complementary to a region 141 bp upstream of the transcription start site; in C, the labeled primer (π858U) was complementary to a region 183 bp downstream of the start site. In lanes 3, 4, 9, and 10, insertional mutants were analyzed by a PCR in which the inserted sequence served as a priming site, as in A. In lanes 5–8 and 11–14, PCR products generated using primers π858U and CAM60supF (one of which was labeled as indicated above) were digested with a restriction endonuclease, whose recognition sequence was unique to the inserted sequence. The ladder (LAD) in lane 15 was generated by pooling 12 unique sequenced clones of replacement mutants that were made in the plasmid πAN13. Ladder DNA was PCR amplified with primer π267L and labeled primer π858U, and digested with a restriction endonuclease as described. (D) The boxed region from lanes 13 and 14 is enlarged to show the PCR products corresponding to substitution mutants replacing all or part of the −10 element. The sequence corresponding to each mutant is indicated to the left with the substituted sequence indicated in boldface type. The wild-type sequence of this region is shown at the bottom, with the −10 element indicated by a box.