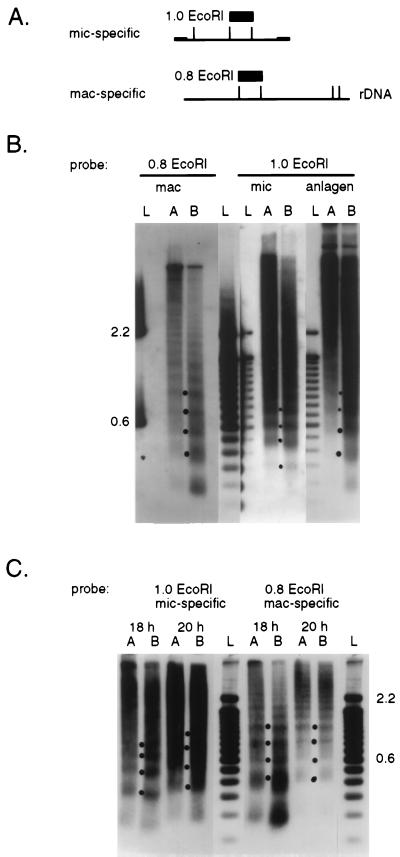
Figure 4.
Micrococcal nuclease digestions of chromatin. (A) Locations of the restriction fragments used as hybridization probes within the 5.3-kb Tec1 element or the 7.5-kb macronuclear rDNA molecule are shown as boxes; the Tec element inverted repeats are shown as small rectangles. (B) Autoradiographs of Southern blot analyses of DNAs derived from micrococcal nuclease-digested chromatin hybridized with either the mic-specific Tec element or mac-specific rDNA probes. Nuclei from vegetative cells (mac and mic) and from mated cells at 28-h postmixing (anlagen) were incubated with micrococcal nuclease for 2 (A lanes) or 10 min (B lanes), and the DNA was extracted and electrophoresed side-by-side with marker DNA fragments (L lanes; the 100-bp ladder from GIBCO/BRL). After Southern blotting, the filter was hybridized with the mic-specific (1.0 EcoRI) probe, stripped, and then hybridized with the mac-specific (0.8 EcoRI) probe. Fragments in the marker lanes were visualized by hybridization with nick-translated 100-bp ladder or, in the case of the rDNA 0.8 EcoRI probe, with the associated plasmid sequences, which hybridized only to the 600-bp and 2.2-kb ladder fragments (labeled to the left). Dots between the A and B lanes indicate the positions of bands corresponding to the dimer, trimer, tetramer, and pentamer nucleosome repeats used to determine spacing. (C) Autoradiographs of Southern blot analyses containing DNA isolated from micrococcal nuclease-digested chromatin from developing cells at either 18 or 20 h of development. Methods and labeling of the figure are as described above.