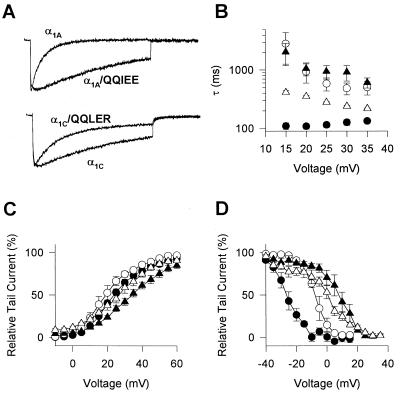
Figure 2.
Effects of mutations in the QXXER motif on voltage-dependent gating of P/Q-type and L-type Ca2+ channels. Control intracellular solutions without GTP[γS] were used in all experiments. (A) Ba2+ currents elicited by a 1000-ms test pulse to +30 mV from a holding potential of −60 mV for the indicated α1 subunits and mutants. (B) Voltage dependence of the time constant for inactivation. Ba2+ currents were recorded during 1000-ms test pulses to the indicated potentials from a holding potential of −60 mV. Currents were fitted with one exponential and the time constants were plotted against the voltage of the test pulse. •, α1A; ○, α1A/QQIEE; ▴, α1C; and ▵, α1C/QQLER. (C) Voltage dependence of activation. Tail currents were recorded at a holding potenial of −60 mV following a 4-ms test pulse to the indicated potential. Tail currents were normalized to the largest tail currents in each series of test pulses, and means ± SEM were plotted as a function of the test voltage. •, α1A; ○, α1A/QQIEE; ▴, α1C; and ▵ α1C/QQLER. (D) Steady-state inactivation. Tail currents were recorded following a 4000-ms prepulse to the indicated potential and a 4-ms test pulse to +30 mV. Tail currents were normalized to the largest tail currents in each series of test pulses, and means ± SEM were plotted as a function of the prepulse voltage. •, α1A; ○, α1A/QQIEE; ▴, α1C; and ▵, α1C/QQLER.