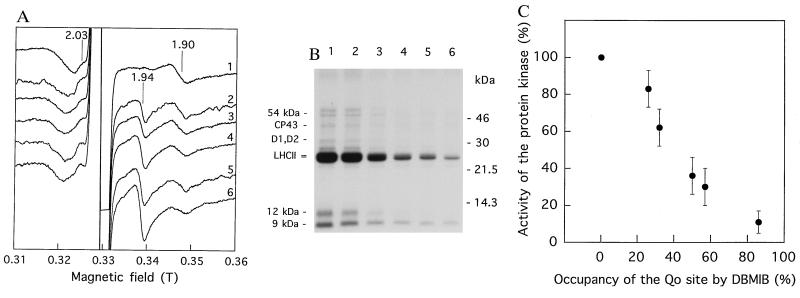
Figure 3.
Deactivation of thylakoid protein phosphorylation due to displacement of plastoquinol from the Qo site by DBMIB. (A) Low-temperature EPR spectra of spinach thylakoid membranes frozen for the EPR measurements after the pH shift in darkness. Preincubation of thylakoids in the acidic medium was done in the absence of DBMIB (trace 1) or in the presence of 3, 6, 9, 12, or 18 μM DBMIB (traces 2–6, respectively); same EPR signal assignment as in Fig. 1. (B) Autoradiogram of SDS/PAGE-resolved thylakoid phosphoproteins. Phosphorylation by [γ-32P]ATP was induced by the pH shift in darkness after preincubation of the membranes in the acidic medium in the absence of DBMIB (lane 1) or in the presence of DBMIB (same concentrations and lane numbering as above, respectively). The concentration of Chl in the final thylakoid suspensions for both A and B was 4 mg/ml. The major phosphoproteins are indicated on the left side of the autoradiogram. (C) Dependence of deactivation of protein kinase (calculated from B) on the occupancy of the Qo site of the cytochrome bf complex by the inhibitor DBMIB as quantified by the shift of the gy Rieske Fe–S center signal from g = 1.90 to g = 1.94 (calculated from A).