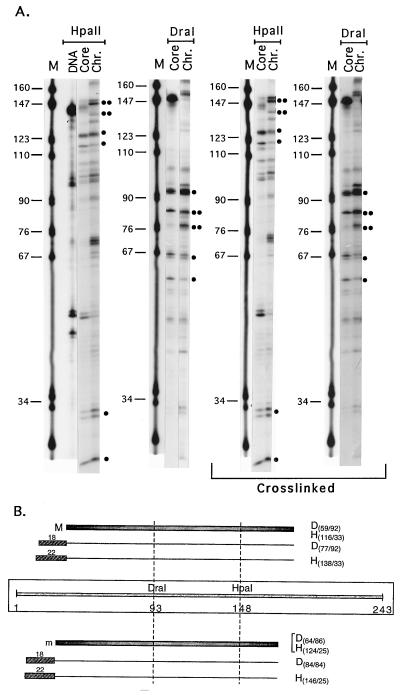
Figure 3.
(A) Linker histone-induced protection of linker DNA against MNase digestion. Lanes: M, pBR322/MspI size markers; Core and Chr., restriction fragments of core- and chromatosome-sized DNA fragments extracted from the MNase gels such as those shown in Fig. 2B. DNA designates lane containing digestion products of the core-sized DNA fragment extracted from MNase digestion gels of naked DNA. Main digestion products identified as representing core or chromatosome positions (see text) are marked by dots. One dot designates fragments seen in either the core nucleosome or in both the core and the chromatosome; two dots designate new fragments observed in chromatosome digests only. The restriction enzymes used are denoted above the respective lanes. Lanes marked crosslinked present the results of the same analysis performed after crosslinking the protein to the DNA at the core nucleosome reconstitution step, before the addition of LH. (B) Scheme summarizing the protection data. The positions of the core particles M and m are denoted as gray bars, and those of the chromatosomes are denoted as plain lines with stippled gray boxes at the end, representing the DNA stretches protected by LH binding. The numbers above these boxes denote the lengths of the protected regions (in bp). The light gray bar in the middle of the scheme represents the DNA fragment used for reconstitution, with the sites for DraI and HpaII cleavage marked accordingly. The pairs of restriction fragments used for the assignments are marked with D (for DraI) or H (for HpaII), followed by numbers denoting the lengths of the fragments, as determined from the sequencing gels.