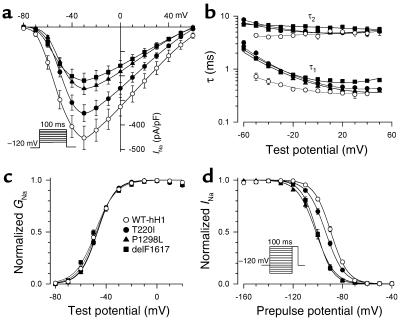
Figure 5.
Impaired fast inactivation in mutant sodium channels. (a) Current-voltage relationship for WT-hH1 (open circles, n = 16), T220I (filled circles, n = 25), P1298L (filled triangles, n = 17), and delF1617 (filled squares, n = 17) sodium channels. Current (in pA) is normalized to cell capacitance (in picofarads, pF) to give a measure of sodium current density. Current density is significantly lower for T220I, P1298L, and delF1617 at test potentials between –60 mV and +60 mV (P < 0.05). (b) Voltage dependence of fast inactivation time constants (τ1 and τ2) for WT-hH1 (open circles, n = 16), T220I (filled circles, n = 25), P1298L (filled triangles, n = 17), and delF1617 (filled squares, n = 17). Lower and upper bundles of symbols indicate τ1 and τ2 values, respectively. Differences between WT-hH1 and mutant channels were significant for τ1 (T220I and P1298L; P < 0.05 at tested voltage between –50 to –10 mV; delF1617, P < 0.05 at all tested voltages). In some cases, error bars are smaller than the data symbol. (c) Voltage dependence of activation for WT-hH1 (open circles), T220I (filled circles), P1298L (filled triangles), and delF1617 (filled squares). Curves were fit with a Boltzmann distribution, and values determined for the voltage midpoint (V1/2) and slope factor (k) are shown in Table 2. G, conductance. (d) Sodium channel availability for WT-hH1 (n = 19), T220I (n = 30), P1298L (n = 32), and delF1617 (n = 12) recorded using the pulse protocol shown in the inset and fit with Boltzmann distributions (solid lines). The half-maximal voltage for Na channel inactivation (V1/2) and slope factor are listed in Table 2.